شناسایی ابعاد و مولفههای برنامه درسی تفکر سیستمی با رویکرد هیوتاگوژی در دوره اول متوسطه
کلمات کلیدی:
شناسایی ابعاد برنامه درسی, تفکر سیستمی, دوره اول متوسطه, هیوتاگوژیچکیده
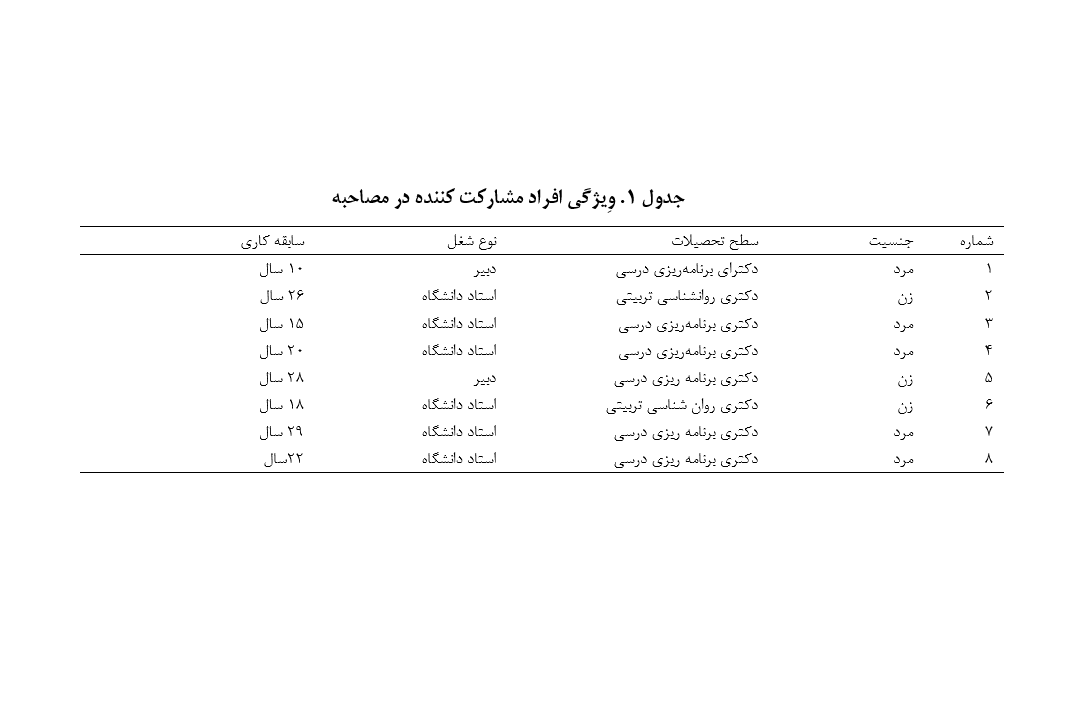
با توجه به نقش مهم برنامه درسی در موفقیت نظام آموزشی، بکارگیری رویکردهای فکری جدید در برنامه درسی باید مورد توجه قرار گیرد، بنابراین پژوهش حاضر با هدف شناسایی ابعاد و مولفههای برنامه درسی تفکر سیستمی با رویکرد هیوتاگوژی در دوره اول متوسطه انجام شد. مطالعه حاضر از نظر هدف کاربردی و از نظر شیوه اجرا کیفی بود. جامعه این پژوهش تعداد8 نفر از متخصصان و اساتید دانشگاه در حوزههای برنامه ریزی درسی و روانشناسی تربیتی بودند که طبق اصل اشباع نظری و با روش نمونه گیری هدفمند و گلوله برفی انتخاب شدند. برای تحلیل دادهها از روش تحلیل مضمون با روش شبکه مضامین استفاده شد. یافتههای حاصل از پژوهش نشان داد برای طراحی الگوی برنامه درسی تفکر سیستمی با رویکرد هیوتاگوژی در دوره اول متوسطه در مضمون فراگیر برنامه درسی، 26 مضمون پایه در 7 مضمون سازماندهنده شامل؛ اصلاح ساختار، مدیریت فرایندها، آموزش نوین، گسترش پژوهشگری، بکارگیری فناوری، آینده نگری و درک پیچیدگیها، در مضمون فراگیر الزامات پیاده سازی، 15 مضمون پایه در 5 مضمون سازمان دهتده شامل؛ ساختار، قانونی، کارکردی، جامع نگری سیستمی در طراحی کلان، درک ابعاد و روابط در فرایندهای تربیتی و در مضمون فراگیر اثرات پیاده سازی 23 مضمون پایه در 8 مضمون سازماندهنده شامل؛ رشد قابلیتهای تحصیلی دانش آموزان، رشد قابلیتهای اجتماعی دانش آموز، بهبود شایستگی روانی دانش آموز، رشد انواع تفکر دانش آموز، درک روابط سیستمی و مدلسازی، سازگاری و درک محیطهای پیچیده، انعطاف پذیری و بهبود شایستگی تدریس معلم شناسایی شدند.
دانلودها
مراجع
Bezi A, Fakoori H, Bayani AA, Saemi H. Design and Validation of an Environmental Education Curriculum Model
for Higher Education Based on the "Aker" Approach. Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology. 2024;7(1):79-90. doi:
61838/kman.ijes.7.1.8.
Song Q. Applying Design Thinking in Ecotourism Curriculum Design: The Educational Design Ladder. Open Journal
of Applied Sciences. 2024;14(06):1454-63. doi: 10.4236/ojapps.2024.146096.
Bansal S, Sherif YA, Nuchtern JG, Rosengart TK, Davis RW. A comprehensive curriculum for the American
academic global surgery trainee: Addressing an educational need. The American Journal of Surgery. 2023;226(5):721-5. doi:
1016/j.amjsurg.2023.06.016.
Yusuf M, Samsura DAA, Yuwono PSH. Toward a framework for an undergraduate academic tourism curriculum in
Indonesian Universities: Some perspectives from stakeholders. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education.
;22:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.02.003.
Kit JA, Fell A. A social-constructivist approach to learning enhanced by technology. Qualitative Education Research.
;11(1):47-58.
Shafii N, editor Self-Determination Curriculum from the Heutagogical Approach Perspective. Fifth International
Conference on Psychology, Educational Sciences, and Lifestyle; 2018.
Shafii N, editor The Position of Teaching Individual Systemic Thinking in Future Schools. Second National
Conference on Future School; 2021.
Jain AB, Sharma L, Sharma N, Jain C, Madaan M. Students' Perception Regarding Pedagogy, Andragogy, and
Heutagogy as Teaching-Learning Methods in Undergraduate Medical Education. Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
;9:1-7. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_221_20.
Hase S. An Introduction to Self-Determined Learning (Heutagogy). In: Blaschke LM, Kenyon C, editors. Experiences
in Self-Determined Learning: Amazon; 2014. p. 1-19.
Hase S, Kenyon C. The nature of learning. In: Hase S, Kenyon C, editors. Self-determined learning: Heutagogy in
action: Bloomsbury; 2013. p. 19-38.
Hainsworth N, Dowse E, Cummins A, Ebert L, Foureur M. Heutagogy: A self-determined learning approach for
midwifery continuity of care experiences. Nurse Education in Practice. 2022;60:103329. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103329.
Lynch M, Sage T, Hitchcock LI, Sage M. A heutagogical approach for the assessment of Internet Communication
Technology (ICT) assignments in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education.
;18(55):1-16. doi: 10.1186/s41239-021-00290-x.
Wehmeyer ML, Shogren KA, Toste JR, Mahal S. Self-Determined Learning to Motivate Struggling Learners in
Reading and Writing. Intervention in School and Clinic. 2017;52(5):295-303. doi: 10.1177/1053451216676800.
Handayani SM, Yeigh T, Jacka L, Peddell L. Developing a heutagogy approach to promoting teacher competencies
in Indonesia. Cypriot Journal of Educational Science. 2021;16(3):939-51. doi: 10.18844/cjes.v16i3.5765.
Mirowski P. From Mandelbrot to chaos in economic theory. Southern Economic Journal. 1990;57(2):289-307. doi:
2307/1060611.
Davis B, Sumara D. Complexity as a theory of education. Transnational Curriculum Inquiry. 2008;5(2).
Assaraf OBZ, Orion N. Systems thinking skills at the elementary school level. Journal of Research in Science
Teaching. 2010;47(5):540-63. doi: 10.1002/tea.20351.
Jaiswal A, Karabiyik T. Characterizing Undergraduate Students' Systems-Thinking Skills through Agent-Based
Modeling Simulation. Sustainability. 2022;14(19):12817. doi: 10.3390/su141912817.
Shaked H, Schechter C. Systems Thinking for Principals of Learning-Focused Schools. Journal of School
Administration Research and Development. 2019;4(1):18-23. doi: 10.32674/jsard.v4i1.1939.
Badurdeen F, Gregory R, Luhan GA, Schroeder M, Vincent LV, Sekulic DP. Systems Thinking for Sustainability:
Envisioning Trans-disciplinary Transformations in STEM Education. Learning. 2012;11:12.
Lally D, Forbes C, editors. Not Specified. School of Natural Resources, University of Nebraska-Lincoln; 2020.
Bosch O, Nguyen N, Sun D. Addressing the critical need for a "new way of thinking" in dealing with complex issues
facing our societies. Business Systems Review. 2013;2:48-70.
Plate R. Assessing individuals' understanding of nonlinear causal structures in complex systems. System Dynamics
Review. 2010;26(1):19-33. doi: 10.1002/sdr.432.
Bogler R, Nir AE. The contribution of perceived fit between job demands and abilities to teachers' commitment and
job satisfaction. Educational Management Administration & Leadership. 2015;43(4):541-60. doi:
1177/1741143214535736.
Aghajani Z. Teaching Systemic Thinking in Secondary School, Teacher's Educational, Analytical, and Informative
Monthly (Special Issue for 12th Grade). Not Specified. 2018.
Dyehouse M, Bennett D, Harbor J, Childress A, Dark M. A comparison of linear and systems thinking approaches for
program evaluation illustrated using the Indiana Interdisciplinary GK-12. Evaluation and Program Planning. 2009;32(3):187-
doi: 10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2009.03.001.
Zoller U. Environmental education and the university: The 'problem solving-decision making act' within a critical
system-thinking framework. Higher Education in Europe. 1990;15:5-14. doi: 10.1080/0379772900150402.
Nikmohammadi Z, Shafii N, Arakiyeh A. Identifying the Dimensions and Components of Heutagogical Curriculum
in Secondary Education. Sociology of Education. 2023;9(2):275-86.
Habibi Asl P. Examining Solutions for Developing the Professional Knowledge of Part-Time Teachers in Bahmai
County Based on Heutagogical, Synergistic, Andragogical, and Pedagogical Approaches: Shiraz Payam Noor University; 2021.
Abili K, Mazari E. Providing a Self-Development Heutagogical Model in an Electronic Context (A Model for Leading
Learning). Digital Journal, Digital Transformation Encyclopedia. 2021;2(1):17-1.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 1403 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










