Identifying the Dimensions and Components of a Systems Thinking Curriculum with a Heutagogical Approach in Lower Secondary Education
Keywords:
Identifying curriculum dimensions, system thinking, first year of high school, hyutagogyAbstract
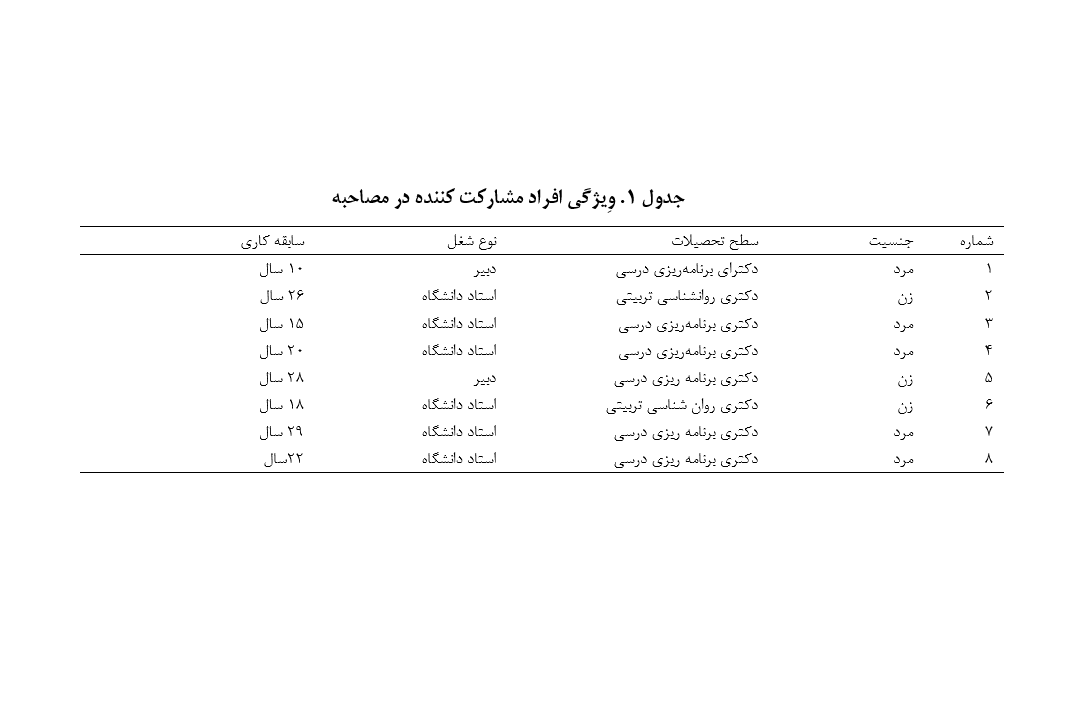
Given the crucial role of curriculum in the success of educational systems, the integration of new cognitive approaches in curriculum design should be considered. Accordingly, the present study aimed to identify the dimensions and components of a systems thinking curriculum with a heutagogical approach in lower secondary education. This study is applied in terms of purpose and qualitative in terms of implementation. The research population included eight experts and university faculty members specializing in curriculum planning and educational psychology, who were selected through purposive and snowball sampling methods based on the principle of theoretical saturation. Thematic analysis using a theme network approach was employed to analyze the data. The findings of the study indicated that for designing a systems thinking curriculum model with a heutagogical approach in lower secondary education, within the overarching theme of curriculum, 26 basic themes were categorized under seven organizing themes: structural reform, process management, modern education, promotion of research, utilization of technology, foresight, and understanding complexity. In the overarching theme of implementation requirements, 15 basic themes were classified under five organizing themes: structural, legal, functional, systemic comprehensiveness in macro design, and understanding dimensions and relationships in educational processes. Furthermore, in the overarching theme of implementation effects, 23 basic themes were identified under eight organizing themes: enhancement of students' academic capabilities, development of students' social competencies, improvement of students' psychological competencies, advancement of students' various thinking skills, understanding systemic relationships and modeling, adaptability and comprehension of complex environments, flexibility, and enhancement of teachers' teaching competencies.
Downloads
References
Bezi A, Fakoori H, Bayani AA, Saemi H. Design and Validation of an Environmental Education Curriculum Model
for Higher Education Based on the "Aker" Approach. Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology. 2024;7(1):79-90. doi:
61838/kman.ijes.7.1.8.
Song Q. Applying Design Thinking in Ecotourism Curriculum Design: The Educational Design Ladder. Open Journal
of Applied Sciences. 2024;14(06):1454-63. doi: 10.4236/ojapps.2024.146096.
Bansal S, Sherif YA, Nuchtern JG, Rosengart TK, Davis RW. A comprehensive curriculum for the American
academic global surgery trainee: Addressing an educational need. The American Journal of Surgery. 2023;226(5):721-5. doi:
1016/j.amjsurg.2023.06.016.
Yusuf M, Samsura DAA, Yuwono PSH. Toward a framework for an undergraduate academic tourism curriculum in
Indonesian Universities: Some perspectives from stakeholders. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education.
;22:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.02.003.
Kit JA, Fell A. A social-constructivist approach to learning enhanced by technology. Qualitative Education Research.
;11(1):47-58.
Shafii N, editor Self-Determination Curriculum from the Heutagogical Approach Perspective. Fifth International
Conference on Psychology, Educational Sciences, and Lifestyle; 2018.
Shafii N, editor The Position of Teaching Individual Systemic Thinking in Future Schools. Second National
Conference on Future School; 2021.
Jain AB, Sharma L, Sharma N, Jain C, Madaan M. Students' Perception Regarding Pedagogy, Andragogy, and
Heutagogy as Teaching-Learning Methods in Undergraduate Medical Education. Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
;9:1-7. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_221_20.
Hase S. An Introduction to Self-Determined Learning (Heutagogy). In: Blaschke LM, Kenyon C, editors. Experiences
in Self-Determined Learning: Amazon; 2014. p. 1-19.
Hase S, Kenyon C. The nature of learning. In: Hase S, Kenyon C, editors. Self-determined learning: Heutagogy in
action: Bloomsbury; 2013. p. 19-38.
Hainsworth N, Dowse E, Cummins A, Ebert L, Foureur M. Heutagogy: A self-determined learning approach for
midwifery continuity of care experiences. Nurse Education in Practice. 2022;60:103329. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103329.
Lynch M, Sage T, Hitchcock LI, Sage M. A heutagogical approach for the assessment of Internet Communication
Technology (ICT) assignments in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education.
;18(55):1-16. doi: 10.1186/s41239-021-00290-x.
Wehmeyer ML, Shogren KA, Toste JR, Mahal S. Self-Determined Learning to Motivate Struggling Learners in
Reading and Writing. Intervention in School and Clinic. 2017;52(5):295-303. doi: 10.1177/1053451216676800.
Handayani SM, Yeigh T, Jacka L, Peddell L. Developing a heutagogy approach to promoting teacher competencies
in Indonesia. Cypriot Journal of Educational Science. 2021;16(3):939-51. doi: 10.18844/cjes.v16i3.5765.
Mirowski P. From Mandelbrot to chaos in economic theory. Southern Economic Journal. 1990;57(2):289-307. doi:
2307/1060611.
Davis B, Sumara D. Complexity as a theory of education. Transnational Curriculum Inquiry. 2008;5(2).
Assaraf OBZ, Orion N. Systems thinking skills at the elementary school level. Journal of Research in Science
Teaching. 2010;47(5):540-63. doi: 10.1002/tea.20351.
Jaiswal A, Karabiyik T. Characterizing Undergraduate Students' Systems-Thinking Skills through Agent-Based
Modeling Simulation. Sustainability. 2022;14(19):12817. doi: 10.3390/su141912817.
Shaked H, Schechter C. Systems Thinking for Principals of Learning-Focused Schools. Journal of School
Administration Research and Development. 2019;4(1):18-23. doi: 10.32674/jsard.v4i1.1939.
Badurdeen F, Gregory R, Luhan GA, Schroeder M, Vincent LV, Sekulic DP. Systems Thinking for Sustainability:
Envisioning Trans-disciplinary Transformations in STEM Education. Learning. 2012;11:12.
Lally D, Forbes C, editors. Not Specified. School of Natural Resources, University of Nebraska-Lincoln; 2020.
Bosch O, Nguyen N, Sun D. Addressing the critical need for a "new way of thinking" in dealing with complex issues
facing our societies. Business Systems Review. 2013;2:48-70.
Plate R. Assessing individuals' understanding of nonlinear causal structures in complex systems. System Dynamics
Review. 2010;26(1):19-33. doi: 10.1002/sdr.432.
Bogler R, Nir AE. The contribution of perceived fit between job demands and abilities to teachers' commitment and
job satisfaction. Educational Management Administration & Leadership. 2015;43(4):541-60. doi:
1177/1741143214535736.
Aghajani Z. Teaching Systemic Thinking in Secondary School, Teacher's Educational, Analytical, and Informative
Monthly (Special Issue for 12th Grade). Not Specified. 2018.
Dyehouse M, Bennett D, Harbor J, Childress A, Dark M. A comparison of linear and systems thinking approaches for
program evaluation illustrated using the Indiana Interdisciplinary GK-12. Evaluation and Program Planning. 2009;32(3):187-
doi: 10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2009.03.001.
Zoller U. Environmental education and the university: The 'problem solving-decision making act' within a critical
system-thinking framework. Higher Education in Europe. 1990;15:5-14. doi: 10.1080/0379772900150402.
Nikmohammadi Z, Shafii N, Arakiyeh A. Identifying the Dimensions and Components of Heutagogical Curriculum
in Secondary Education. Sociology of Education. 2023;9(2):275-86.
Habibi Asl P. Examining Solutions for Developing the Professional Knowledge of Part-Time Teachers in Bahmai
County Based on Heutagogical, Synergistic, Andragogical, and Pedagogical Approaches: Shiraz Payam Noor University; 2021.
Abili K, Mazari E. Providing a Self-Development Heutagogical Model in an Electronic Context (A Model for Leading
Learning). Digital Journal, Digital Transformation Encyclopedia. 2021;2(1):17-1.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 1403 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










