Validation of the Educational Corruption Model in Universities
Keywords:
corruption, educational corruption, Higher Education, validationAbstract
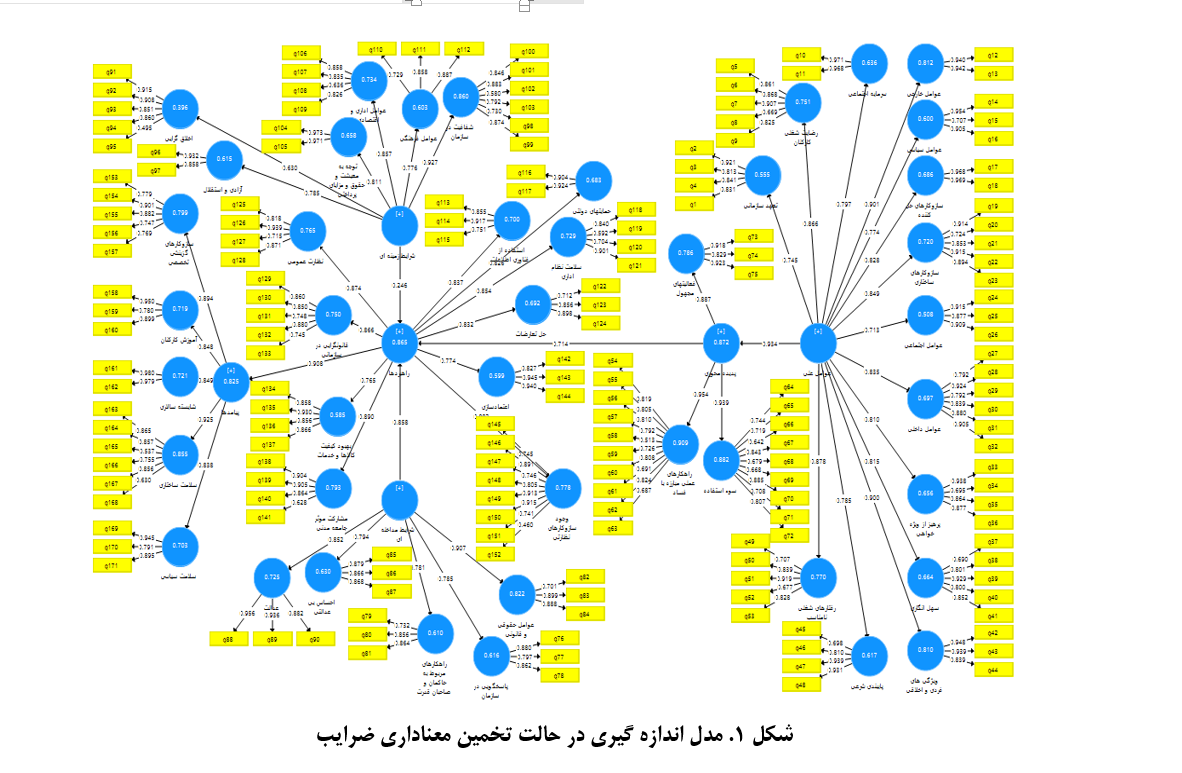
Corruption in general, and educational corruption specifically, is a disruptive factor in the development of various societal sectors. The aim of the present study was to validate an educational corruption model in universities. This research was a quantitative-survey study and, in terms of its purpose, was applied. The statistical population included 384 employees of universities and higher education institutions, selected through random sampling. The research tool was a researcher-developed questionnaire based on qualitative findings and the literature review. Structural equation modeling with PLS Smart software was used for data analysis. The results indicated that in the quantitative evaluation of the model, all values were significant, greater than 1.96, and the standardized coefficients were greater than 0.4, confirming the model. Given that the goodness of fit index was 0.626, the final model was confirmed. Accordingly, the impact coefficient of strategies on outcomes (0.90 and t-value of 1.07), the impact of contextual conditions on strategies (24.6 and t-value of 4.7), the impact of intervening conditions on strategies (0.85 and t-value of 1.46), the impact of causal factors on the central phenomenon (93.4 and t-value of 14.6), and the impact of the central phenomenon on strategies (0.714 and t-value of 14.9) were observed. It can be concluded that corruption is a multi-dimensional issue, and higher education policymakers should focus on identifying its causes based on various research results, including the findings of this study, in order to establish and foster corruption-free higher education.
Downloads
References
Bagherimajd K, Khajedad K, Mahmoudi F. Design of a model to reduce academic corruption in higher education.
International Journal of Ethics Education. 2024:1-25. doi: 10.1007/s40889-024-00197-x.
Heliany I, Asmadi E, Sitinjak H, Lubis AF. The Role Of Corruption Education In Combating Corruption Crimes In
The Future. JPH. 2023;10(2):11-22. doi: 10.26532/jph.v10i2.32344.
Waite D, Allen D. Corruption and abuse of power in education administration. The Urban Review. 2003;35:281-96.
doi: 10.1023/B:URRE.0000017531.73129.4f.
Rumyantseva NL. Taxonomy of corruption in higher education. Peabody Journal of Education. 2005;80(1):81-92.
doi: 10.1207/S15327930pje8001_5.
Nye JS. Corruption and political development: A cost-benefit analysis. American Political Science Review.
;61(2):417-27. doi: 10.2307/1953254.
Jin X, Bin F. Analysis of the reasons and countermeasures for academic corruption. Chinese Education & Society.
;40(6):95-105. doi: 10.2753/CED1061-1932400613.
Rafipour F. The social cancer of corruption. Tehran: Sohami Publishing; 2009.
Osipian AL. University autonomy in Ukraine: Higher education corruption and the state. Communist and PostCommunist Studies. 2017;50(3):233-43. doi: 10.1016/j.postcomstud.2017.06.004.
Hashemzadeh DH, Fazeli M, Mohadesi-Gilviee H. Measuring Academic Corruption: A Multi-dimentional Model.
Journal of Iranian Social Studies. 2016;10(4):116-48.
Sabic-El-Rayess A, Heyneman SP. Education and corruption. Education and Corruption2020.
Persists WC. Inequality, education, and corruption. The Oxford handbook of the quality of government2021. p. 427-
Denisova-Schmidt E. Introduction: Corruption in Higher Education: Global Challenges and Responses. Corruption
in Higher Education2020. p. 1-12.
Heyneman SP. Corruption in the education sector. Handbook on Corruption, Ethics and Integrity in Public
Administration. Edward Elgar Publishing2020. p. 129-38.
Silova I, Bray M. The hidden marketplace: Private tutoring in former socialist countries. Education in a hidden
marketplace: Monitoring of private tutoring2006. p. 71-98.
Yang R. Corruption in China's higher education: a malignant tumor. International Higher Education. 2005(39):18-9.
doi: 10.1080/10611932.2005.11031720.
Deliversky J. Preventing corruption in the education system. Journal of Educational and Instructional Studies in the
World. 2016;6(1):141-6.
Santizo Rodall CA, Martin CJ. School‐based management and citizen participation: lessons for public education from
local educational projects. Journal of Education Policy. 2009;24(3):317-33. doi: 10.1080/02680930802669268.
Danaifard H. Anti-Corruption Strategy: Does Information Technology Reduce Corruption? Management Research in
Iran. 2021;9(2):101-17.
Seifzadeh A. Investigating citizens' perception of administrative corruption and demographic variables affecting it
(case study: Birjand). Khorasan Social Cultural Studies. 2016;10(4):114-93.
Yun A. Corruption in Uzbek higher education: Detrimental impurity for the future. Central Asia Policy Briefs.
;34.
Mohammadian K, Salimi J, Azizi N, Mohamadi S. Structural roots of the occurrence of academic corruption in higher
education in Iran. Journal of Educational Sciences. 2020;27(2):159-82. doi: 10.22055/edus.2021.33499.3031.
Rabiei A. Long live Corruption (Political Sociology of Corruption in Third World Governments). Tehran: Printing
and Publishing Organization and Ministry of Culture and Islamic Guidance; 2003.
Atshak M, Ghahrani M, Abolghasemi M, Farastkhah M. The concept of administrative corruption in the public
education system. Ethics in Science and Technology. 2014;6(3):33-47.
Rashidi A, Raisi L. Corruption and Its Impact on Human Rights. Quarterly Journal of Social Development.
;11(4):237-54. doi: 10.22055/qjsd.2017.13013.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










