طراحی مدل تلفیقی یادگیری مشارکتی برای تدریس درس ریاضی: یک مرور سیستماتیک
کلمات کلیدی:
تدریس , درس, ریاضی, مرور, سیستماتیک, یادگیری , مشارکتیچکیده
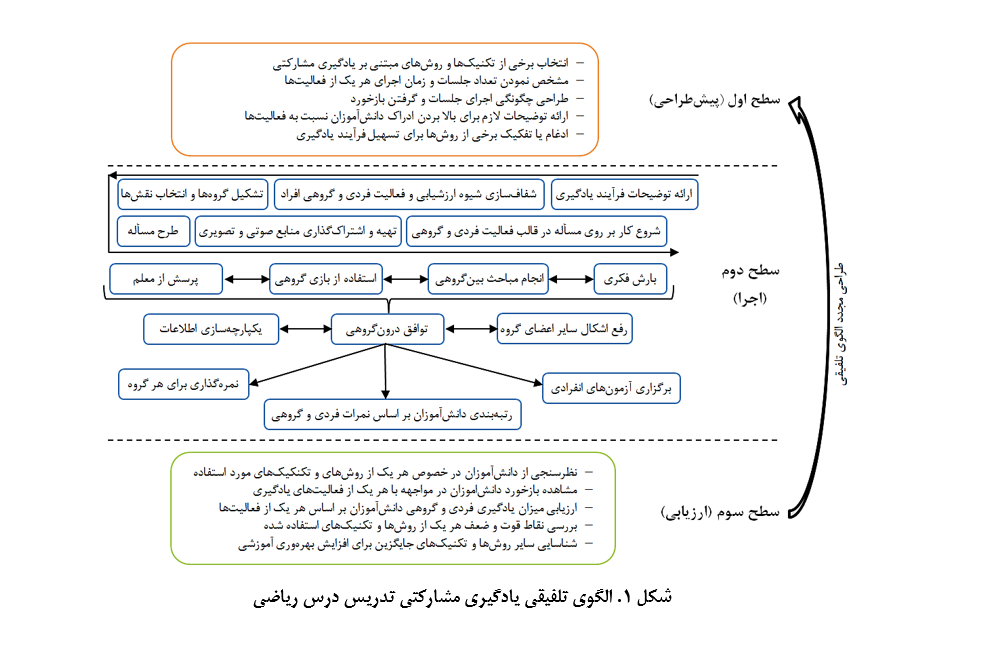
هدف این مطالعه، شناسایی سبکهای یادگیری مشارکتی برای تدریس ریاضی و ارائه یک چارچوب مفهومی بر اساس رویکرد اوکولی و شابرام (2010) برای یک مرور سیستماتیک است. برای انجام این مطالعه، مقالات مرتبط با کلیدواژههای «یادگیری مشارکتی»، «سبک یادگیری مشارکتی»، «ریاضی»، «تدریس ریاضی» و «آموزش ریاضی» در پایگاههای داخلی و بینالمللی در بازه زمانی پنجساله تا سال 2023 بررسی شدند. از عملگرهای منطقی «و» و «یا» برای افزایش دقت جستجو استفاده شد. پس از بررسی معیارهای ورود و خروج، 45 مقاله مرتبط شناسایی و سبکها و استراتژیهای یادگیری مشارکتی ارزیابی شدند. نتایج نشان داد که 36 مطالعه بهصورت کمی، 7 مطالعه بهصورت کیفی و 1 مطالعه با روش آمیخته انجام شدهاند. 21 سبک یادگیری مشارکتی با 29 معیار اصلی شناسایی شد که بیشترین تکرار مربوط به یادگیری مبتنی بر حل مسئله و روش جیگساو بود. این دو روش بهعنوان مبنای اصلی مدل نهایی در نظر گرفته شدند و سایر استراتژیها برای تقویت مدل به آن اضافه شدند. فرایند تدریس در سه سطح پیشطراحی، اجرا و ارزیابی سازماندهی شد. تدریس اثربخش ریاضی نیازمند فضایی پویا است که در آن دانشآموزان مهارتهای فردی و گروهی خود را تقویت کنند. استفاده از یادگیری مشارکتی موجب پرورش تفکر انتقادی و علمی میشود و کیفیت آموزش را بهبود میبخشد. یافتههای این پژوهش میتوانند در بهبود آموزش مدارس، ارتقای کیفیت تدریس معلمان و افزایش انگیزه و توانایی شناختی دانشآموزان مفید باشند. معلمان با دور شدن از روشهای سنتی و استفاده از تکنیکهای مشارکتی مانند بارش فکری، بازیهای گروهی و رقابتهای آموزشی میتوانند علاقه دانشآموزان به یادگیری ریاضی را افزایش دهند. طراحان کتب آموزشی و دورههای ضمن خدمت نیز میتوانند از این مدل در بهبود روشهای آموزشی استفاده کنند.
دانلودها
مراجع
Asarta CJ, Schmidt JR. Comparing student performance in blended and traditional courses: Does prior academic achievement matter? The Internet and Higher Education. 2017;32:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.08.002.
Nekonam V. Requirements for Investigating the Privacy of Communicative and Informative Data in Cyberspace. New Technologies Law. 2024;5(9):27-40.
Nelson AE. Methods faculty use to facilitate nursing students’ critical thinking. Teaching and Learning in Nursing. 2017;12(1):62-6. doi: 10.1016/j.teln.2016.09.007.
Kong L. Collaborative learning and academic performance in lyceum of the Philippines university-Batangas city senior high school. International Journal of Frontiers in Sociology. 2021;3(2).
Keramati MR. Collaborative learning and academic progress with a metacognitive approach. Tehran: Zengeh Shad Publications. 2016.
Lock J, Johnson C. Triangulating assessment of online collaborative learning. Quarterly Review of Distance Education. 2015;16(4):61.
Zakaria NI, Iksan ZH. Computational thinking among high school students. Universal Journal of Educational Research. 2020;8(11).
Fitzpatrick B, Ali SI. Cooperative learning: Value-added to operations management. International Journal of Management & Information Systems (IJMIS). 2011;15(2):31-8. doi: 10.19030/ijmis.v15i2.4150.
Tarawneh SH. The effect of using the cooperative teaching method on achievement in mathematics and the attitude toward it for female students of the eighth basic grade. Damascus University Journal. 2012;28(3):449-71.
Ahmedabadi A, Zeinabadi HR, Ostadrahimi M. The effect of teaching with the reverse method in comparison with the methods of cooperation, exploration and lecture on the learning of experimental sciences of sixth grade elementary students. Policy studies of teacher training. 2021;4(1).
Arabi A, Ozra A, Azimi I, Emamjome SMR. Collaborative prototyping method of digital educational games with design thinking approach in promoting 6th grade math learning: barriers, facilitators and solutions. Theory and Practice in Curriculum Quarterly. 2023;11(21):70-39.
Boye ES, Agyei DD. Effectiveness of problem-based learning strategy in improving teaching and learning of mathematics for pre-service teachers in Ghana. Social Sciences & Humanities Open. 2023;7(1):100453. doi: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2023.100453.
Al-Jalali LM. Academic achievement: Al-Masira for; 2011.
Jalali R, Khazaei H, Paveh BK, Hayrani Z, Menati L. The effect of sleep quality on students’ academic achievement. Advances in medical education and practice. 2020:497-502. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S261525.
Peker M. Mathematics teaching anxiety and self-efficacy beliefs toward mathematics teaching: A path analysis. Educational Research and Reviews. 2016;11(3):97-104. doi: 10.5897/ERR2015.2552.
Jameson MM, Fusco BR. Math anxiety, math self-concept, and math self-efficacy in adult learners compared to traditional undergraduate students. Adult Education Quarterly. 2014;64(4):306-22. doi: 10.1177/0741713614541461.
Aghajani S, Khormaee F, Rajabi S, Rostamoqli Khiavi Z. The relationship of self-esteem and self-efficacy to mathematical anxiety in students. Journal of School Psychology. 2012;1(3):6-26.
Foley AE, Herts JB, Borgonovi F, Guerriero S, Levine SC, Beilock SL. The math anxiety-performance link: A global phenomenon. Current directions in psychological science. 2017;26(1):52-8. doi: 10.1177/0963721416672463.
Diani AH, Dwijanto D. Mathematical creative thinking ability observed from student learning motivation in Jigsaw Cooperative Learning assisted by problem cards. Unnes Journal of Mathematics Education. 2020;9(1):66-73. doi: 10.15294/ujme.v9i1.38102.
Wang Z, Lukowski SL, Hart SA, Lyons IM, Thompson LA, Kovas Y, et al. Is math anxiety always bad for math learning? The role of math motivation. Psychological science. 2015;26(12):1863-76. doi: 10.1177/0956797615602471.
Rump M, Esdar W, Wild E. Individual differences in the effects of academic motivation on higher education students’ intention to drop out. European Journal of Higher Education. 2017;7(4):341-55. doi: 10.1080/21568235.2017.1357481.
Gill AC, Singhal G, Schutze GE, Turner TL. Educational Coaches: Facilitating Academic Vitality and a Pathway to Promotion for Clinician-Educators. The Journal of Pediatrics. 2021;235:3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.042.
Senobar A, Kasir S, TaghaviNasab A, Raeisi E. The role of cognitive and metacognitive learning strategies, academic optimism and academic engagement in predicting academic vitality of nursing students. Education Strategies in Medical Sciences. 2018;11(2):149-55.
Hajihoseinlou K, Khaleghkhah A, Zahedbabolan A, Moenikia M. The effect of cooperative learning with achievement groups on self-efficacy and self-concept of student’s mathematics. Educational psychology. 2017;13(43):119-39.
Habibi-Kaleybar R. Studing the effectiveness of teaching the thinking and research lesson in a collaborative way on creative thinking and reading skills of primary schools’ sixth grade students. Thinking and Children. 2018;8(2):1-20.
Marashi H, Khatami H. Using cooperative learning to boost creativity and motivation in language learning. Journal of Language and Translation. 2017;7(1):43-58.
Polat Ö, Sezer T, Akyol NA. Collaborative learning with mind mapping in the development of social skills of children. Participatory Educational Research. 2022;9(1):463-80. doi: 10.17275/per.22.25.9.1.
Purba SF. The Effect of STAD Cooperative Learning on Mathematical Representation Ability and Student Interests. JMEA: Journal of Mathematics Education and Application. 2022;1(1):44-53.
Vrcelj A, Hoic-Božic N, Dlab MH. Use of gamification in primary and secondary education: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Educational Methodology. 2023;9(1):13-27. doi: 10.12973/ijem.9.1.13.
Purwanto R. Increasing student motivation and learning outcomes in coordination system competency through the teaching game team learning method for class XI Science students at SMA Smart Ekselensia Indonesia for the 2010-2011 academic year. Dompet Dhuafa Education Journal. 2011;1(1):1-14.
Susanto A. Learning and Learning Theory in Elementary Schools. Prenadamedia. 2013.
Chrisnawati HE, Pramesti G, Kuswardi Y, Cortez CP, Osenar-Rosqueta AMF, Prudente MS. A comparative study on mathematics teaching and learning in teacher professional education programs: Understanding students’ mathematical concepts in zoning school Cooperative-flipped classroom under online modality: Enhancing students’ mathematics achievement and critical thinking attitude. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2019;2194(1):102213. doi: 10.1016/j.ijer.2023.102213.
Okoli C, Schabram K, Ork M, Saif MH. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research The effect of collaborative learning on academic achievement, attitude and anxiety in mathematics. The 8th conference of modern studies and researches in the field of educational sciences, psychology and counseling in Iran. 2010.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










