شناسایی و اولویتبندی عوامل مؤثر بر بازماندگی از تحصیل در نظام آموزش و پرورش در ایران
کلمات کلیدی:
بازماندگی از تحصیل, نظام آموزش و پرورش, عوامل خانوادگی, عوامل فرهنگی, عوامل اجتماعیچکیده
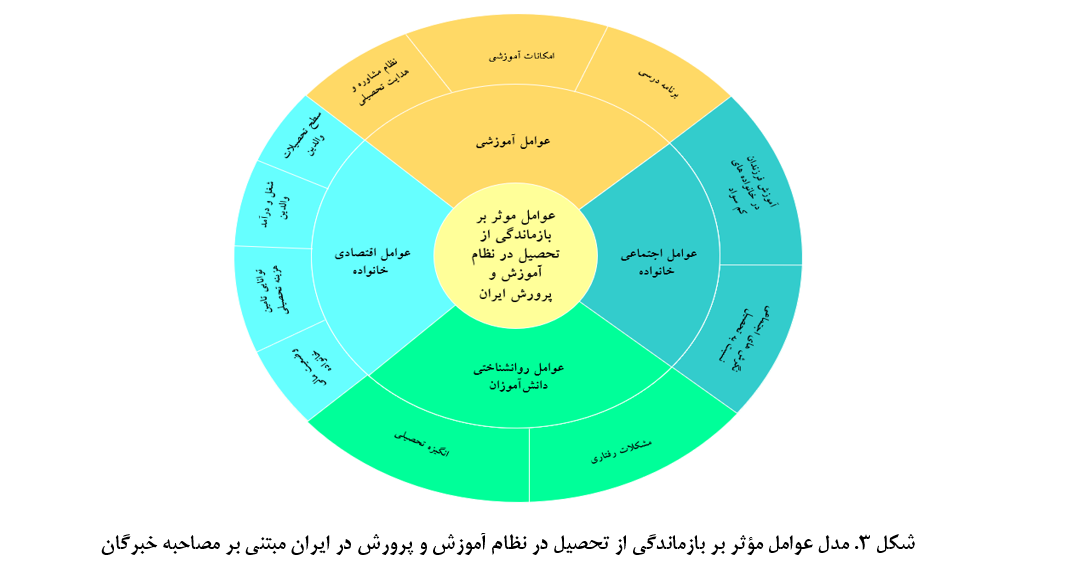
پژوهش حاضر با هدف شناسایی و اولویتبندی عوامل مؤثر بر بازماندگی از تحصیل در نظام آموزش و پرورش در ایران انجام شد. این پژوهش به لحاظ هدف، کاربردی و همچنین، به لحاظ نوع دادهها، آمیخته که به لحاظ ماهیت تحلیل محتوا متون مصاحبه بود. جامعه آماری شامل خبرگان در زمینه بازماندگی از تحصیل بودند. در بخش تحلیل محتوا حجم نمونه 15 مصاحبهشونده با توجه به اصل اشباع و روش نمونهگیری هدفمند بودند. در بخش تحلیل محتوا، برای محاسبه روایی سوالهای مصاحبه از نظر خبرگان مورد بررسی قرار گرفت و برای محاسبه پایایی از توافق بین دو کدگذار، توافق درون آزمودنی و در بخش کمی در مورد پرسشنامه مقایسه زوجی برای روایی از روایی محتوا و برای پایایی از نرخ سازگاری استفاده شد که نتایج بیانگر روا و پایا بودن ابزارها بود. روش تجزیه و تحلیل دادهها، در بخش کیفی تحلیل مضمون (مضامین پایه، سازماندهنده و فراگیر) با نرمافزار MaxQDA-V2018 و در بخش کمی برای اولویتبندی از فرایند تحلیل سلسلهمراتبی با استفاده از نرمافزار Expertchoice-V11 استفاده شد. یافتهها نشان داد عوامل مؤثر بر بازماندگی از تحصیل در نظام آموزش و پرورش در ایران به ترتیب اولویت شامل عوامل اقتصادی خانواده (0.355)، عوامل اجتماعی خانواده (0.273)، عوامل روانشناختی دانشآموزان (0.209) و عوامل آموزشی (0.163) است.
دانلودها
مراجع
Farmonovna SF. The Importance of Students' Economic Competences in Improving the Quality of Education.
Interdiscipline Innovation and Scientific Research Conference2023. p. 48-50.
Ortiz-Wythe B, Warren MR, King AR. Intersectional Organizing and Educational Justice: How Lived Experience
Influences Community Organizers' Understanding and Practice of Intersectional Organizing. Soc Sci. 2022;11(147):1-23. doi:
3390/socsci11040147.
UNESCO. Derecho a la Educación Bajo Presión: Principales Desafíos y Acciones Transformadoras en la Respuesta
Educativa al Flujo Migratorio Mixto de Población Venezolana en Perú. 2020.
Mohammadi R, Namvar Y, Rastgoo A, Kheirkhah M, Salimi T. Explaining Educational Justice in Medical
Universities: A Grounded Theory Study. Jundishapur Journal of Educational Development. 2022;13(2):497-509.
Garcés-Velástegui P. Modelling Amartya Sen's Capability Approach: An Interdisciplinary and Contemporary
Account. 2022.
Govaris C, Kassis W, Sakatzis D, Sarafidou J-O, Chouvati R. Recognitive Justice and Educational Inequalities: An
Intersectional Approach Involving Secondary Grade School Students in Greece. Educ Sci. 2021;11(461). doi:
3390/educsci11090461.
Eurydice Report E. Integrating Students from Migrant Backgrounds Education and Training into Schools in Europe.
Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA, Education and Youth Policy Analysis), 2019.
Warren MR. Willful Defiance: The Movement to Dismantle the School-to-Prison Pipeline. New York: Oxford
University Press; 2022.
Miyazaki Y, Du C, Papadopoulos J, Du H. Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated with Left Behind Children in
China. Asian Social Science. 2020;16(10):1. doi: 10.5539/ass.v16n10p1.
Huang Y, Gong H. Educational Expectations of Left-Behind Children in China: Determinants and Gender Differences.
Jin Z, Han B, He J, Huang X, Chen K, Wang J, Liu Z. Unintentional Injury and Its Associated Factors Among LeftBehind Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Psychiatry. 2023;23(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04964-w.
Zhou C, Lv Q, Yang N, Wang F. Left-Behind Children, Parent-Child Communication and Psychological Resilience:
A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
;18(10):5123. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105123.
Gao AZ, Chen WC. The Association Between Internet Use and Cognitive Ability Among Rural Left-Behind Children
in China. Frontiers in Public Health. 2024;11. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1341298.
Lee J, Zhou M. The Asian-American Achievement Paradox. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2015.
Lumayag LA. A Question of Access: Education Needs of Undocumented Children in Malaysia. Asian Studies Review.
;40(2):192-210. doi: 10.1080/10357823.2016.1158238.
Justus A. 6 Reasons - Why Children in India Drop Out of School and Become Child Labourers. World Vision
International, 2015.
Heydari A, Sedaghat M, Mirzaei A. Processes of Production and Reproduction of School Dropout in Sistan and
Baluchestan Province. Strategic Research on Iran's Social Issues. 2022;11(2):47-70.
Aref Nejad V. Examination of Barriers and Methods of Attracting Children Who Have Dropped Out of School in
Rural and Nomadic Areas (A Mixed Study). Applied Education Research Center of Tabriz, Educational Studies Research
Institute, Educational Research and Planning Organization, 2016.
Könemann J. Educational Justice. Education Science. 2017;7(53). doi: 10.3390/educsci7020053.
Brighouse H, Swift A, Meyer K. The Place of Educational Equality in Educational Justice. Education, Justice, and
the Human Good. London: Routledge; 2014. p. 14-33.
Iuliana Ioanaa M, Andaa MI, Petroman C, Ciolac RM. School Dropout - A Social Problem in Romania. Procedia -
Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015;182:623-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.04.795.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2024 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










