ارائه مدلی برای ارتقای هوش اجتماعی اعضای هیئت علمی دانشگاه فرهنگیان تهران
کلمات کلیدی:
هوش, هوش اجتماعی, اعضای هیات علمی, دانشگاه فرهنگیانچکیده
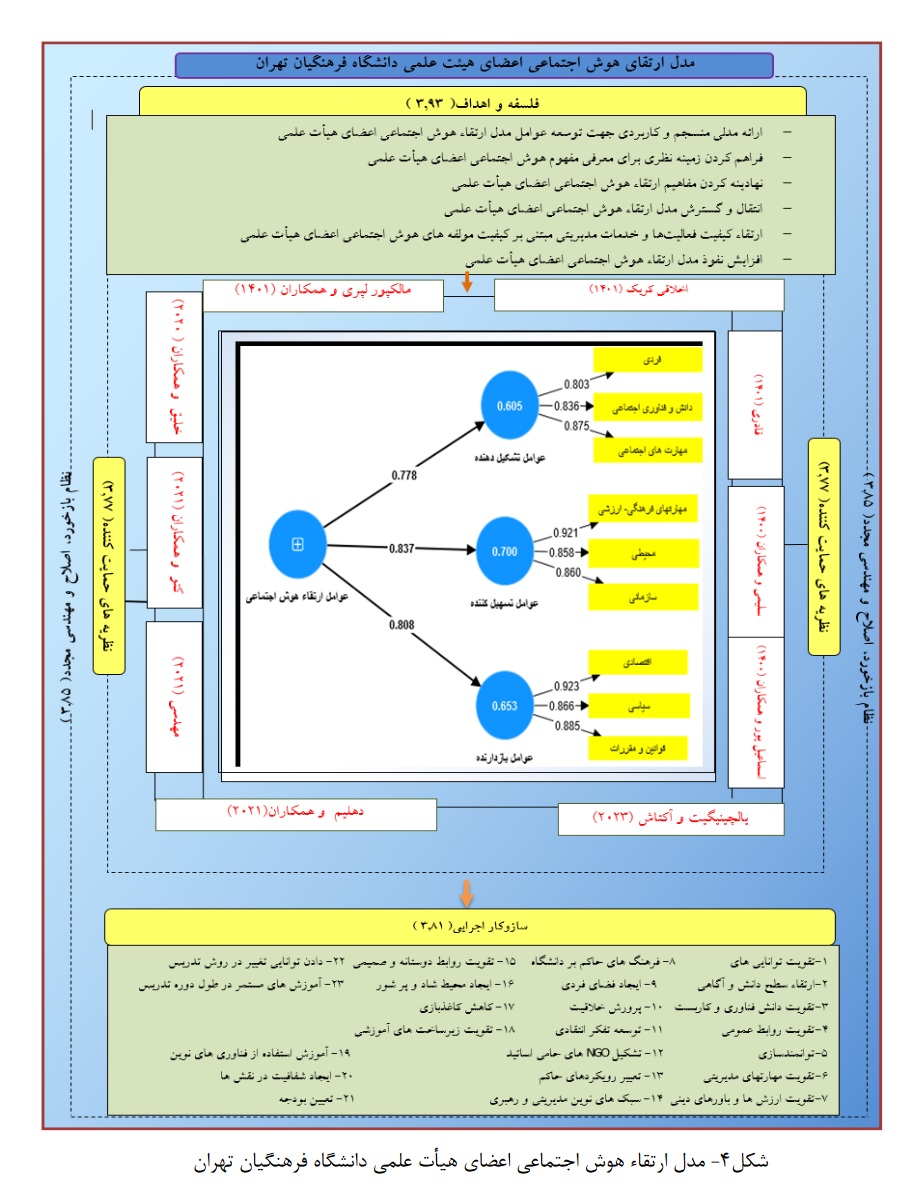
هدف اصلی این مقاله ارائه مدلی برای ارتقای هوش اجتماعی اعضای هیئت علمی دانشگاه فرهنگیان تهران است. روش انجام پژوهش آمیخته(کیفی-کمی) است. برای انجام این پژوهش علاوه بر مطالعۀ اسنادی، از تکنیک تحلیل مضمون با نرم افزار MAXQDA12 ، برای شناسایی ابعاد و مولفه ها استفاده شده است. جامعه آماری در این پژوهش تمام خبرگان در حوزه مدیریت آموزشی و مدیریت فرهنگی و مدیریت منابع انسانی همچنین خبرگان امر روانشناسی اجتماعی بودند که بعد از انجام 20 مصاحبه اشباع نظری صورت گرفت و تمام مصاحبه ها بین 75 تا 120 دقیقه به طول انجامید. در نهایت مضامین پایه، سازمان دهنده و فراگیر استخراج گردید و در بخش کمی برای تعیین وضعیت موجود و سهم ابعاد و مولفه ها از روش توسعه ای با استفاده از نرم افزار معادلات ساختاری ( pls ) بهره گرفته شده است. با توجه به مصاحبه های نیمه ساختار یافته، 55 شاخص، 9 مولفه و 3 بُعد برای عوامل تشکیل دهنده و 3 بُعد و 7 مولفه و 42 شاخص برای عوامل تسهیل کننده و 3 بُعد و 6 مولفه و 17 شاخص برای عوامل بازدارنده برای رتقاء هوش اجتماعی در میان اعضای هیأت علمی دانشگاه فرهنگیان تهران استخراج گردید. و براساس ضرایب بدست آمده از روش معادلات ساختاری عوامل تسهیل کننده با ضریب 0.837 اولویت اول و عوامل بازدارنده با ضریب 0.808 در اولویت دوم و عوامل تشکیل دهنده با ضریب 0.778 در اولویت سوم قرار دارد و در نهایت از روش اعتباریابی درونی با 4 بُعد (فلسفه و اهداف، مبانی نظری، نظام ارزیابی، سازوکاراجرایی) مورد تایید خبرگان قرار گرفت.
دانلودها
مراجع
Gottfredson LS. Where and why g matters: Not a mystery. Human Performance. 2022;15(1):24-46. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327043HUP1501&02_03.
Eini Pour J, Aghaei A, Rezazadeh A. Predicting Attitude Towards Responsibility Based on Sense of Coherence and
Social Intelligence (Case Study: Police Commanders in Counties). Knowledge and Research in Applied Psychology.
;22(3):97-106.
Moran S, Kornhaber M, Gardner H. Orchestrating multiple intelligence. Journal of Educational Leadership.
;64(1):22-7.
Riggio RE, Reichard RJ. The emotional and social intelligences of effective leadership. Journal of Managerial
Psychology. 2018;23(2):169-85. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/02683940810850808.
Wallenius M, Punamaki RL, Rimpela A. Digital Game Playing and Direct and Indirect Aggression in Early
Adolescence: The Roles of Age, Social intelligence, and Parent-Child Communication. Journal of Youth Adolescence.
;36(3):325-36. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-006-9151-5.
Buzan T. The power of social intelligence. New York, NY: Perfect Pound Publisher; 2012. 127-39 p.
Esmaeilpour H, Bazavind Z, Rastgar A. The Mediating Role of Social Intelligence in the Relationship between
Knowledge Management and Organizational Wisdom in Employees of Payam Noor Universities in Fars Province. Journal of
Applied Educational Leadership. 2021;2(1):65-76. doi: https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.ijimob.2.1.3.
Zargoush S, Gheisaribeigi Z, Zargoush F, Mirzaei M. Investigating the Impact of Social Intelligence on the Academic
Achievement of Students. Modern Advances in Psychology. 2020;33(2):78-87.
Miłkowski M. Social intelligence: How to integrate research? A mechanistic perspective. AI & SOCIETY.
;34(4):735-44. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-017-0787-3.
Ahmadi Zadeh Shahrebabaki M, Safidgari S, Abdi A. Comparison of Social Intelligence and Religious Orientation
among Gifted and Regular Female High School Students in Karaj. Journal of Psychological and Educational Studies.
(3):64-71.
Björkqvist K, Österman K, Kaukiainen A. Social intelligence−Empathy= aggression? Aggression and Violent
Behavior. 2020;5(2):191-200. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-1789(98)00029-9.
Mohammadi Pouya F, Qarloghi S, Mohammadi Pouya S, Gharib Tazra S. Investigating the Relationship Between
Social Intelligence and Graduate Students' Perception of Classroom Structure and the Mediating Role of Self-Efficacy Beliefs.
Scientific Research Bimonthly on Educational Strategies in Medical Sciences. 2018;11(4):1-8.
George A, Jayanthi NLN. A Study on Social Intelligence of High School Students. Journal of the Gujarat Research
Society. 2019;21(14):36-9.
Haji Aghanajad Y, Zare Nistank M, Dadashi M. The Relationship Between Creativity and Social Intelligence in
Students of Allameh Tabataba'i University and Shahid Beheshti University. Military Care Sciences. 2019;6(1):68-1. doi:
https://doi.org/10.29252/mcs.6.1.61.
Promsri C. The Effects of Social Intelligence on Workplace Spirituality. Journal of Advances in Social Science and
Humanities. 2019;5(5):755-62.
Mohadesi E. An examination of the relationship between social intelligence and organisational commitment among
the school managers of Kashmar and Khalilabad. Global Journal of Guidance and Counseling in Schools: Current Perspectives.
;11(2):98-109. doi: https://doi.org/10.18844/gjgc.v11i2.5705.
Crowne KA. The relationship among social intelligence, emotional intelligence and cultural intelligence. Journal of
Organization Management. 2019;6(3):148-63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1057/omj.2009.20.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2024 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










