Identifying and Prioritizing Factors Influencing the Ranking of Schools in Iraq from Stakeholders’ Perspectives
Keywords:
School ranking, ranking from the perspective of stakeholders, schools in IraqAbstract
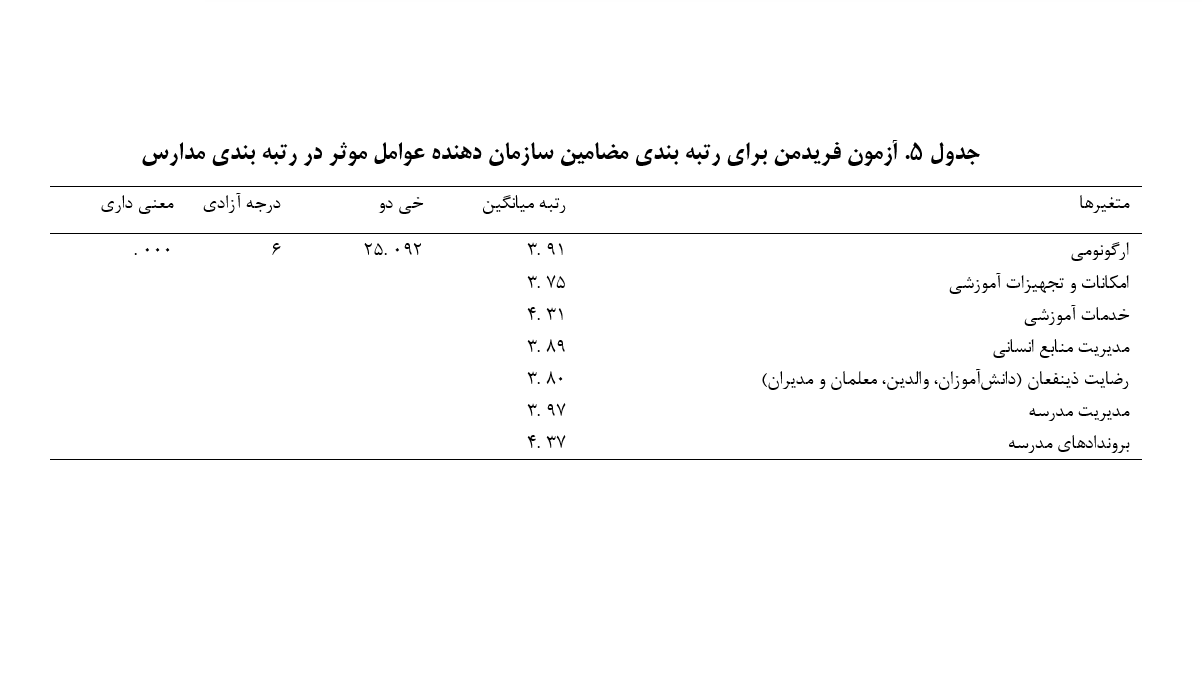
The present study identifies and prioritizes factors influencing the ranking of schools in Iraq’s education system from stakeholders’ perspectives. This research adopts a mixed-method approach involving various groups, including school principals, teachers, and members of parent-teacher associations. In the qualitative phase, factors influencing school rankings were identified through semi-structured interviews and thematic analysis. The data were transformed into initial codes and basic themes, which were then categorized into organizing themes and one overarching theme. To validate the model, methods such as participant feedback and reviewing academic sources were employed. The reliability of the findings was confirmed through expert committee feedback and calculating the Content Validity Index (CVI) and Content Validity Ratio (CVR). In the quantitative phase, a questionnaire was developed and distributed among 282 individuals, including principals, teachers, and parent-teacher association members. Using a one-sample t-test, the agreement level of participants regarding the extracted factors was assessed. Finally, the factors were ranked using the Friedman test. Results revealed a total of 76 key themes grouped into 10 components: ergonomics, educational facilities and resources, educational services, human resource management, stakeholder satisfaction (students, parents, teachers, and principals), school management, and school outputs.
Downloads
References
Cheng Y-C. A Typology of Multiple School Leadership. Education Sciences. 2024;14(1):70. doi: 10.3390/educsci14010070.
Abella J, Kilag OK, Andrin G, Tañiza FN, Groenewald E, Cordova Jr N. Literacy Leadership in Elementary Schools: The Connections between Principal Practices and Reading Performance. Excellencia: International Multi-disciplinary Journal of Education. 2024;2(1):69-78.
Zare Banadkouki MR, Vahdat Zad MA, Olya MS, Lotfi MM. Pathology of university ranking systems from the perspective of higher education superordinate documents in Iran. Educational Management Research. 2017;20(1):52-87.
Hassani R, Jamali A, Taghipour Zaheer A, Rahgozar M. Construction and factor analysis of the measurement model for ranking the country's secondary schools. Educational Management Research. 2017;32(8):41-63.
Delaney JM, Devereux PJ. High school rank in math and English and the gender gap in STEM. Labour Economics. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.labeco.2021.101969.
Bozorginejad K, Zarei R, Amirianzadeh M, Kheir M. Identifying criteria and indicators for ranking private schools from the perspective of strategic factors. Scientific Quarterly Journal of School Management. 2020;8(1):1-15.
Rah Najat M, Negarestani MH. Examining Educational Justice in Light of the Law on the Establishment and Management of Private Schools and Educational Centers. Public Policy Quarterly. 2024;10(1):143-57.
Joshi P. The growth, roles and needs of the private education system: Private stakeholder perspectives from Nepal. International Journal of Educational Development. 2019;65:57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2019.01.002.
Marques M, Powell JJ. Ratings, rankings, research evaluation: How do schools of education behave strategically within stratified UK higher education? 2019. doi: 10.1007/s10734-019-00440-1.
Anderson T, Blom E, Lindsay C. Identifying high-performing schools for historically underserved students: Urban Institute; 2020.
Delprato M, Chudgar A. Factors associated with private-public school performance: Analysis of TALIS-PISA link data. Educational Development. 2018;61:155-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2018.01.002.
Sammons P, Gu Q, Day C, Ko J. Exploring the impact of school leadership on pupil outcomes: Results from a study of academically improved and effective schools in England. International Journal of Educational Management. 2011;25(1):83-101. doi: 10.1108/09513541111100134.
Requier F, Fournier A, Rome Q, Darrouzet E. Science communication is needed to inform risk perception and action of stakeholders. Environmental Management. 2020;257:109983. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109983.
Zardasti L, Yahaya N, Noor NM, Valipour A. Quantifying reputation loss of pipeline operator from various stakeholders' perspectives-Part 1: Prioritization. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2019.104034.
Pasquier U, Few R, Goulden MC, Hooton S, He Y, Hiscock KM. "We can't do it on our own!"-Integrating stakeholder and scientific knowledge of future flood risk to inform climate change adaptation planning in a coastal region. Environmental Science & Policy. 2020;103:50-7. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2019.10.016.
Barrett P, Treves A, Shmis T, Ambasz D, Ustinova M. The impact of school infrastructure on learning: A synthesis of the evidence: The World Bank; 2019.
Mirkamali SM, Saadati Tabar F. Investigating the satisfaction of stakeholders with the in-service training process in the Industrial Development and Renovation Organization of Iran. Training and Human Resource Development. 2015(7):101-23.
Pineo H, Moore G. Built environment stakeholders' experiences of implementing healthy urban development: An exploratory study. Cities & Health. 2021:1-15. doi: 10.1080/23748834.2021.1876376.
Chilton AS, Masur JS. What should law school rankings measure and how should we measure it: A comment on Heald & Sichelman's rankings. Jurimetrics. 2019.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










