Design and Validation of the Redundant Curriculum Model from the Perspective of Elementary School Teachers
Keywords:
Design, Model, Program, Lesson, Excess, Teachers, Course, ElementaryAbstract
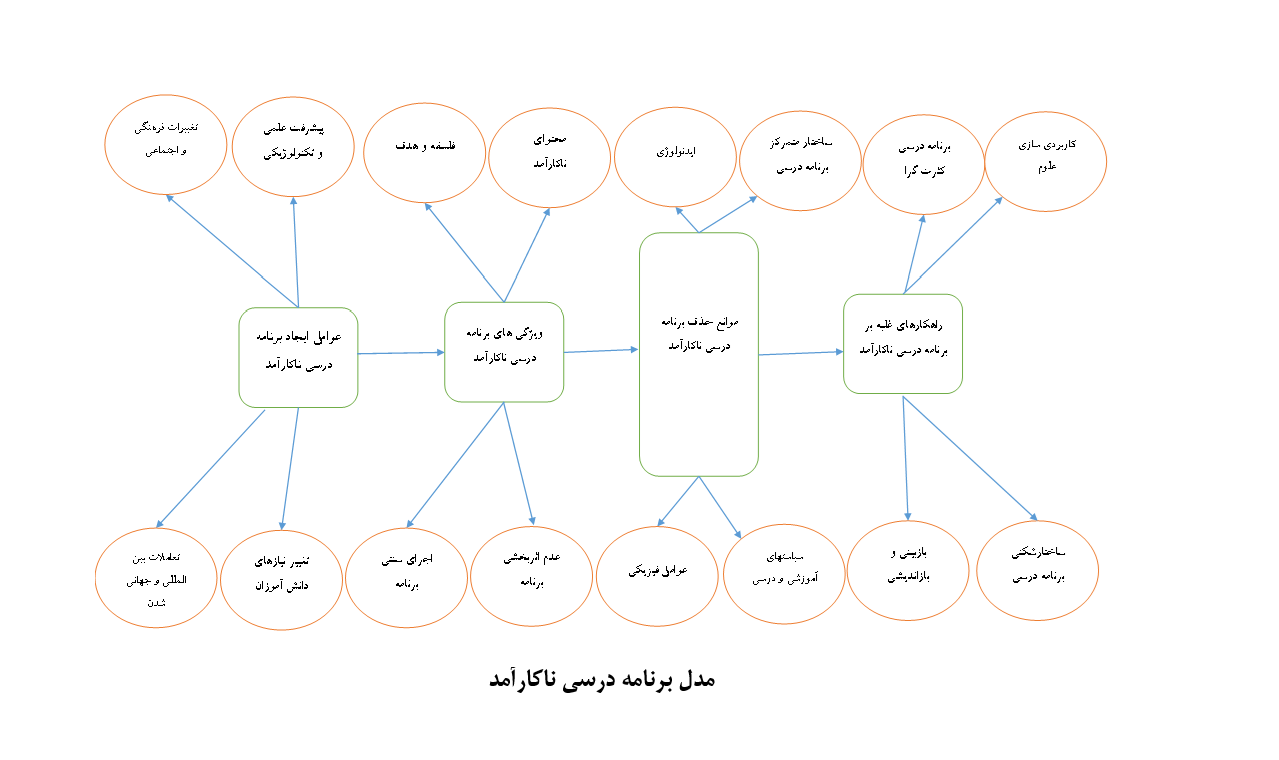
The aim of this study was to design and validate a redundant curriculum model from the perspective of elementary school teachers. The present research follows a sequential exploratory mixed-methods design of the instrumentation type. The qualitative phase was conducted using the phenomenological method and Colaizzi's content analysis approach. Data collection employed purposive sampling of the criterion-based type. Based on the theoretical saturation principle, data collection reached saturation with the 27th participant. The data collection instrument in the qualitative phase consisted of in-depth semi-structured interviews. The credibility of the findings was established through Guba and Lincoln’s criteria, and the reliability of the interviews was calculated using intra-subject agreement. The quantitative phase followed a descriptive survey design. The statistical population in this phase included teachers and curriculum planning experts who had published articles and conducted studies related to the research topic. Using purposive sampling, 220 elementary school teachers and 25 curriculum planning experts from Isfahan Province were selected. Data were collected through a researcher-developed questionnaire. To assess the validity of the designed questionnaire, content validity and construct validity methods were employed. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was used to determine the reliability of the questionnaire, which yielded an overall reliability of 0.89. Confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling were utilized for data analysis. The findings from the qualitative phase identified four main themes: factors contributing to an ineffective curriculum, characteristics of an ineffective curriculum, barriers to eliminating an ineffective curriculum, and strategies for overcoming an ineffective curriculum. Additionally, the quantitative results confirmed the validity of the proposed model from the perspective of experts.
Downloads
References
Hosseini Largani SM, Fathi Vajargah K. Conceptualizing Superfluous Learning in Iran's Higher Education System. Curriculum Studies in Higher Education. 2018.
Hosseini Largani SM, Fathi Vajargah K, Arefi M, Zarafshani K. Conceptualizing Superfluous Learning and Strategies for Reducing It in Iran's Higher Education System from the Perspective of Higher Education Experts. Journal of Educational Measurement and Evaluation Studies. 2015;5(9):33-9.
Fathi Vajargah K. Superfluous/Disposable Curriculum 2011.
Taziki Z, Mahmoud Firouzi Moghadam AK, Hossein Momeni M. Analysis of the Seventh Grade Persian Textbook Compared to the Art Book in Terms of Communication Skills and Capabilities. Journal of Islamic Art Studies. 2022;19(47):70-90.
Mattox JR. Scrap Learning and Manager Engagement: Www.clomedia.com; 2011.
Kuraev A. Soviet higher education: An alternative construct to the western university paradigm. Higher Education. 2016:181-93. doi: 10.1007/s10734-015-9895-5.
Moran E, Seaneen S, Elaine W, Laura T. Exploring restorative practices: Teachers' experiences with early adolescents. International Journal of Educational Research Open. 2024;6:100323. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedro.2024.100323.
Parhizkar L. Explaining the Various Dimensions of the Curriculum (Hidden, Superfluous, and Empty) of Environmental Education in Secondary Schools to Provide Solutions for Enhancing Students' Environmental Literacy: Shahid Beheshti University, Faculty of Educational Sciences and Psychology; 2019.
Murai Y, Juan AYS. Making as an opportunity for classroom assessment: Canadian maker educators' views on assessment. International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction. 2024;39:100631. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcci.2023.100631.
Hassanpour Dehnavi GR, Momeni Mohammadi H, Zirak M, Ajjam AA. Designing and Validating a Superfluous Curriculum Model with a Mixed Approach (Case Study: Curriculum of Technical and Vocational Schools in Secondary Education). Innovations in Educational Management. 2021;17(4):60-75.
Halimi A, Sayyedeh Esmat R, Vahid F. Investigating the Impact of Superfluous Curriculum on Advancement Goals (Educational and Skill Domains) and Empowering Students in Medical Sciences in Mazandaran Province. Quarterly Journal of Jundi Shapur Education Development. 2021;12(1):268-80.
Salehi M, Dehghani M, Khatat M. Reflections on the Superfluous Curriculum in the Primary Education Field. Theory and Practice in Curriculum. 2023;11(21):38-9.
Hasanefendic S, Heitor M, Horta H. Training students for new jobs: The role of technical and vocational higher education and implications for science policy in Portugal. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 2016:328-40. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2015.12.005.
Bacchini D, Esposito C, Affuso G, Amodeo AL. The impact of personal values, gender stereotypes, and school climate on homophobic bullying: A multilevel analysis. Sexuality Research and Social Policy. 2021;18(3):598-611. doi: 10.1007/s13178-020-00484-4.
Bourke S, Burgman I. Coping with bullying in Australian schools: How children with disabilities experience support from friends, parents, and teachers. Disability and Society. 2020;25(3):359-71. doi: 10.1080/09687591003701264.
Momeni Mahmooei H, Hassanpour Dehnavi GR, Zirak M, Ajjam AA. Exploring the Dimensions of the Superfluous Curriculum in the Second Cycle of Technical and Vocational Education. Bi-Monthly Scientific-Research Journal of Strategies in Medical Sciences. 2021;14(2):72-81.
Bray M, Alexandre V. Multiple systems, multiple shadows: Diversity of supplementary tutoring received by private-school students in Dubai. International Journal of Educational Development. 2023;92:102624. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2022.102624.
Vigren H, Jenni A, Leena Maria H, Emmanuel OA, Nancy LC. Teaching immigrant students: Finnish teachers' understandings and attitudes. Teaching and Teacher Education. 2022;114:103689. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2022.103689.
Zulhernanda W. Teachers' perceptions on application of 2013 curriculum for elementary school in Medan. Advances in Language and Literary Studies. 2018;9(1):62-6. doi: 10.7575/aiac.alls.v.9n.1p.62.
Altinyelken HK. Curriculum change in Uganda: Teacher perspectives on the new thematic curriculum. International journal of educational development. 2010;30(2):151-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijedudev.2009.03.004.
Sajoudi A. Comparative Analysis of the Role and Contribution of Each Element of the Curriculum in Shaping and Reducing Superfluous Learning from the Perspective of Students at Dezful Parsay Universities: Kashan University; 2017.
Barshan A, Safaie Moahed S, Valiollah F, Kiamanesh A, Moghadam Zadeh A. Factors Influencing the Formation of Superfluous Learning in In-Service Training: A Qualitative Study. Qualitative Research in Health Sciences. 2018;7(4):418-27.
Yasemi S, Hosseini Khah A, Kian M. A Reflection on the Characteristics of Creativity-Based Curriculum in Primary Education. Research in Primary Education. 2022;4(7):1-19.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sajjad Izadi (Author); Mehdi Keshavarzi (Corresponding author); Farzaneh Vasefian (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










