eComplexity: Validation and Structural Equation Analysis of the Complex Thinking Scale
Keywords:
Systemic thinking, scientific thinking, critical thinking, innovative thinking, structural equationsAbstract
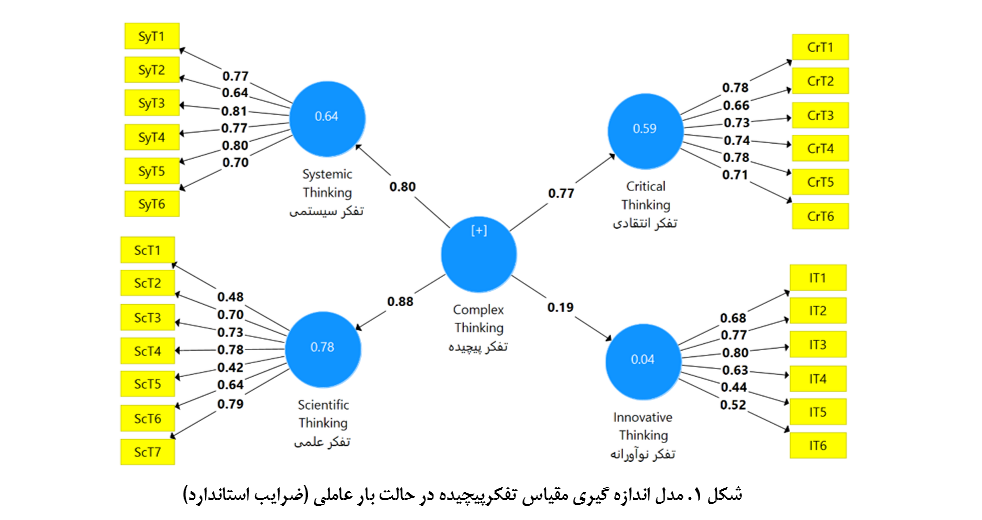
This study aims to validate The Electronic Complexity instrument which aims to measure the perception of success in complex thinking competency and its dimensions. The research method is descriptive. The questionnaire on the quality of the Electronic Complexity instrument developed by Castillo Martínez and Ramírez Montoya (2022) was distributed and evaluated among 270 students from faculties of educational sciences and psychology in Tehran. In the data analysis section, confirmatory factor analysis was used to assess the validity and reliability of the questionnaire. Validity was measured using factor loadings, average variance extracted (AVE), and the Fornell and Larcker method. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 28 and SmartPLS version 3. The results of the exploratory factor analysis indicated that by extracting four components from a total of 25 questionnaire items, these four components explained 52% of the total variance of the questions. The results of the confirmatory factor analysis test demonstrated appropriate factor loadings for the items and confirmed both discriminant and convergent validity. Additionally, reliability was confirmed using composite reliability, indicator reliability, and Cronbach’s alpha. The evaluation of the structural model revealed that the correlation strength between the components and the final construct of complex thinking ranged from a minimum of 0.19 for the innovative thinking component to a maximum of 0.88 for the scientific thinking component, with all relationships being statistically significant (p < .05). This instrument can be reliably used as a valid assessment tool.
Downloads
References
Bancin A, Ambarita B, editors. Education model based on life skill (a Meta- synthesis)2019.
Alt D, Naamati L, Weishut D. Competency-based learning and formative assessment feedback as precursors of college
students' soft skills acquisition. Stud High Educ. 2023;48:1901-17. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2023.2217203.
AlMunifi A, Aleyani A. Knowledge and skills level of graduate civil engineers employers and Graduates' perceptions.
Int J Eng Pedagog. 2019;9:84-101. doi: 10.3991/ijep.v9i1.9744.
Riahi S. Strengthening the teaching of soft skills in the pedagogical architecture of Moroccan universities. Int J Eng
Pedagog. 2022;12:47-62. doi: 10.3991/ijep.v12i4.22329.
Castillo-Martínez I, Ramírez-Montoya M, Torres-Delgado G. Reasoning for complexity competency instrument (ecomplexity): Content validation and expert judgment. Cogent Education. 2024.
Wild S, Schulze L. Re-evaluation of the D21-digital-index assessment instrument for measuring higher-level digital
competencies. Stud Educ Eval. 2021;68:100981. doi: 10.1016/j.stueduc.2021.100981.
Rutherford-Hemming T. "Content validity ratio" in The SAGE encyclopedia of educational research, measurement,
and evaluation: SAGE Publications; 2018.
Baena J, Ramírez M, Mazo D, López E. Traits of complex thinking: a bibliometric review of a disruptive construct in
education. J Intelligence. 2022;10:3. doi: 10.3390/jintelligence10030037.
Horn A, Scheffelaar A, Urias E, Zweekhorst M. Training students for complex sustainability issues: a literature review
on the design of inter- and transdisciplinary higher education. Int J Sustain High Educ. 2022;24:1-27. doi: 10.1108/IJSHE-03-
-0111.
Silva C, Iturra C. A conceptual proposal and operational definitions of the cognitive processes of complex thinking.
Think Skills Creat. 2021;39:100794. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100794.
Silva C, Iturra C. Development and validation of the complex thinking assessment. Think Skills Creat.
;48:101305. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2023.101305.
Vázquez-Parra J, Castillo-Martínez I, Ramírez-Montoya M, Millán A. Development of the perception of achievement
of complex thinking: a disciplinary approach in a Latin American student population. Educ Sci. 2022;12:5. doi:
3390/educsci12050289.
Vázquez-Parra J, Cruz-Sandoval M, Carlos-Arroyo M. Social entrepreneurship and complex thinking: a bibliometric
study. Sustain For. 2022;14:20. doi: 10.3390/su142013187.
Vázquez-Parra JC, Alfaro-Ponce B, Guerrero-Escamilla J, Morales-Maure L. Cultural imaginaries and complex
thinking: impact of cultural education on the development of perceived achievement of complex thinking in undergraduates.
Soc Sci. 2023;12:272. doi: 10.3390/socsci12050272.
Cruz-Sandoval M, Vázquez-Parra JC, Carlos-Arroyo M, Del Angel-González M. Complex thinking and its relevance
in professional training: an approach to engineering students in a Mexican university. Int J Eng Pedagog. 2023;13:100-19. doi:
3991/ijep.v13i3.36885.
Cui L, Zhu Y, Qu J, Tie L, Wang Z, Qu B. Psychometric properties of the critical thinking disposition assessment test
amongst medical students in China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21:10. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02437-2.
Carlos-Arroyo M, Vázquez-Parra J, Cruz-Sandoval M, Echaniz-Barrondo A. Male chauvinism and complex thinking:
a study of Mexican university students. Societies. 2023;13:5. doi: 10.3390/soc13050104.
Castillo-Martínez IM, Ramírez-Montoya MS. eComplexity: Medición de la percepción de estudiantes de educación
superior acerca de su competencia de razonamiento para la complejidad. Monterrey. 2022.
Abuabara L, Paucar A, Werne K, Villas D. Enhancing systemic thinking by sharing experiences of reading literary
fiction using causal mapping. J Oper Res Soc. 2023;75:158-72. doi: 10.1080/01605682.2023.2180448.
Koerber S, Mayer D, Osterhaus C, Schwippert K, Beate S. The development of scientific thinking in elementary
school: a comprehensive inventory. Child Dev. 2015;86:327-36. doi: 10.1111/cdev.12298.
Koerber S, Osterhaus C. Individual differences in early scientific thinking: assessment, cognitive influences, and their
relevance for science learning. J Cogn Dev. 2019;20:510-33. doi: 10.1080/15248372.2019.1620232.
Saienko N, Olizko Y, Cunha A. Perceptions of fostering creative thinking skills in ESP classrooms in Ukraine and
Portugal. Int J Eng Pedagog. 2021;11:23-41. doi: 10.3991/ijep.v11i4.20129.
Luna J, Tobón S, Juárez L. Sustainability-based on socioformation and complex thought or sustainable social
development. Resourc Environ Sustain. 2020;2:100007. doi: 10.1016/j.resenv.2020.100007.
Ramírez-Montoya M, Castillo-Martínez I, Sanabria J, Miranda J. Complex thinking in the framework of education
0 and open innovation-a systematic literature review. J Open Innov: Technol Mark Complex. 2022;8:4. doi:
3390/joitmc8010004.
Diana N, Latifah S, Yuberti Komikesari H, Rohman MH, Tiyan L. Developing an e-learning-based critical-thinking
assessment as a physics learning evaluation media with Kahoot! Interactive quiz. J Phys Conf Ser. 2021;1796:012055. doi:
1088/1742-6596/1796/1/012055.
Tobón S, Luna J. Complex thinking and sustainable social development: validity and reliability of the COMPLEX-21
scale. Sustain For. 2021;13:12. doi: 10.3390/su13126591.
Ossa-Cornejo C, Palma-Luengo M, Lagos-San Martín N, Díaz-Larenas C. Critical and scientific thinking assessment
in preservice teachers at a Chilean university. Rev Electron Educ. 2018;22:1-18. doi: 10.15359/ree.22-2.12.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










