Identifying Curriculum Elements Based On Shahab Plan Elements (Case Study: Elementary School Students)
Keywords:
Curriculum, Shahab Plan, Elementary SchoolAbstract
Background and Purpose: The Shahab plan, which is a plan to improve the quality of education in Iran, is of particular importance in developing the curriculum. Identifying curriculum elements based on the elements of this plan such as goal, content, method and evaluation is necessary to improve the quality of education and achieve effective learning results. These explanations show the need for detailed and comprehensive research in this field in order to provide effective solutions to improve the current situation. Therefore, according to what has been said, this research aimed to identify the elements of the curriculum based on the elements of the Shahab plan in primary school students.
Methodology: This research was applied in terms of purpose, qualitative in terms of data type, cross-sectional in terms of data collection time, and content analysis of interview texts in terms of data collection method or the nature and method of the research. The statistical population included theoretical and experimental experts and the sample size was 19 interviewees according to the principle of saturation and purposeful sampling method. The data collection tools were systematic review of documentary studies and semi-structured interviews. To calculate the validity of the interview questions according to the experts and to calculate the reliability, the agreement between the two coders and the intra-subject agreement were used, and the validity and reliability of the tools were confirmed. The method of data analysis was theme analysis (basic, organizing and overarching themes) with MaxQDA-2018 software.
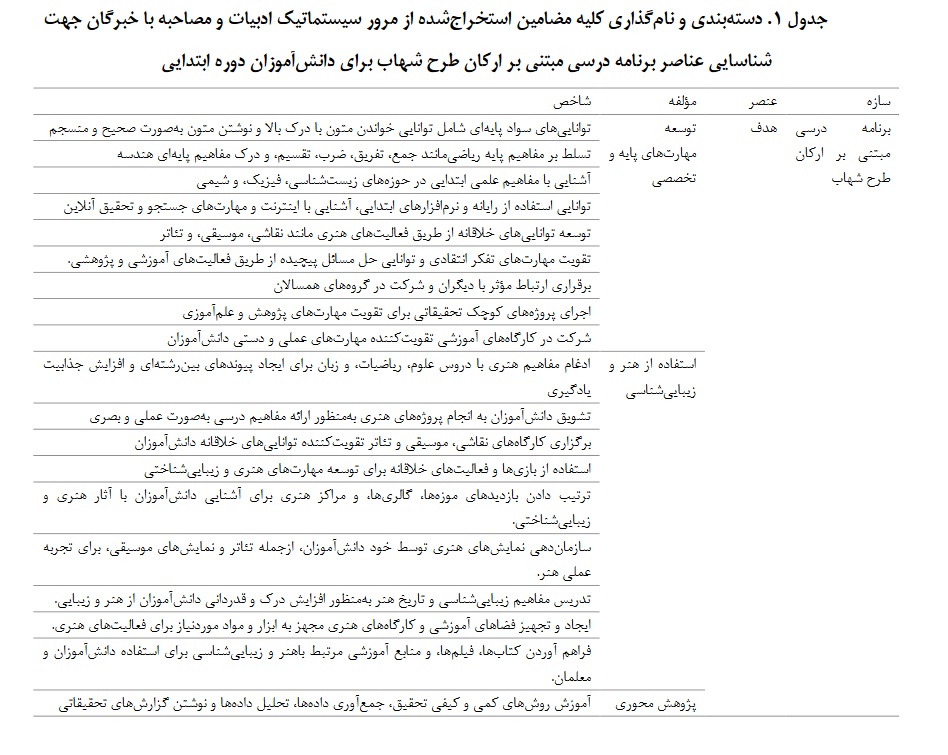
Findings: The findings showed that the curriculum based on Shahab plan included 4 elements: goal, content, method and evaluation. The target element includes the components of developing basic and specialized skills (9 indicators), using aesthetic art (9 indicators), central research (7 indicators), providing a learning environment (9 indicators); The content element includes challenging and complex components (3 indicators), curriculum compression (5 indicators), designing alternative learning experiences (5 indicators); The element of the method includes the components of talent identification (7 indicators), rich learning environments (4 indicators), creativity and innovation training (4 indicators) and the evaluation element including the components of cognitive ability (3 indicators), personality traits (4 indicators), academic achievements (3) index) and executive and leadership abilities (4 indices).
Conclusion: The results of the current research can improve the quality of education, increase the motivation and participation of students, and improve the skills of teachers. By accurately identifying curriculum elements, educational goals are clearly defined, and content and teaching methods are adapted to the needs of learners. This leads to a more effective and engaging learning environment where students can easily acquire the necessary skills and knowledge. Also, more accurate and effective assessments can help to identify the strengths and weaknesses of learners and ultimately lead to the improvement of the overall quality of education at the primary level.
Downloads
References
Razmjooei Z, Rahmani A. Learning resources in education. New Achievements in Humanities Studies. 2023;6(66):34-
Dehghani M. Analysis and critique of the book "Fundamentals of Curriculum Planning in Elementary Education".
Critical Research Journal of Humanities Texts and Curricula. 2023;113:65-88.
Asefi M, Abbasian H, Zeinabadi HR. Pathology of Shahab National Plan in Primary Schools of Shahryar, Iran. Iranian
journal of educational sociology. 2022;5(3):195-213. doi: 10.61186/ijes.5.3.195.
Mehr Mohammadi M. Curriculum: Perspectives, Approaches, and Prospects. Tehran: SAMT; 2014.
Gedifew MT. Instructional Leadership Development Practices in Ethiopia: Curriculum Development and
Implementation Practices, and Career Development Frameworks. Journal of School Leadership. 2023;33(1):50-65. doi:
1177/10526846221134005.
Null W. Curriculum: From theory to practice. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.; 2011.
VanTassel-Baska J, Wood SM. The integrated curriculum model. Systems and models for developing programs for
the gifted and talented: Routledge; 2023. p. 655-91.
Taheri Zadeh S, Shabani R. Localized Curriculum, an Indispensable Necessity for Multi-Grade Classes. Research in
Curriculum Planning. 2019;63:66-77.
Hooshmandi M, editor Curriculum planning and its role in elementary education. National Conference on New
Achievements in Education, Psychology, Law, and Cultural-Social Studies; 2018.
Farmonovna ON, editor ON THE HELP OF MOTIVATION IN LEARNING ENGLISH. Proceedings of International
Conference on Modern Science and Scientific Studies; 2023.
Khoobchehreh M, Akbari A, Pourshafei H, Cherabin M. Identification and prioritization of dimensions and
components of standard education. Journal of Educational Leadership and Management. 2018;12(1):87-110.
Tang C, Mao S, Xing Z, Naumann S. Improving student creativity through digital technology products: A literature
review. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2022:101032. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2022.101032.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










