تاثیر تعامل با همتایان و نفوذ اجتماعی بر یادگیری درک شده دانش آموزان دوره ابتدایی با نقش میانجی درگیری
کلمات کلیدی:
Peer interaction, social influence, perceived learning, academic engagement, elementary studentsچکیده
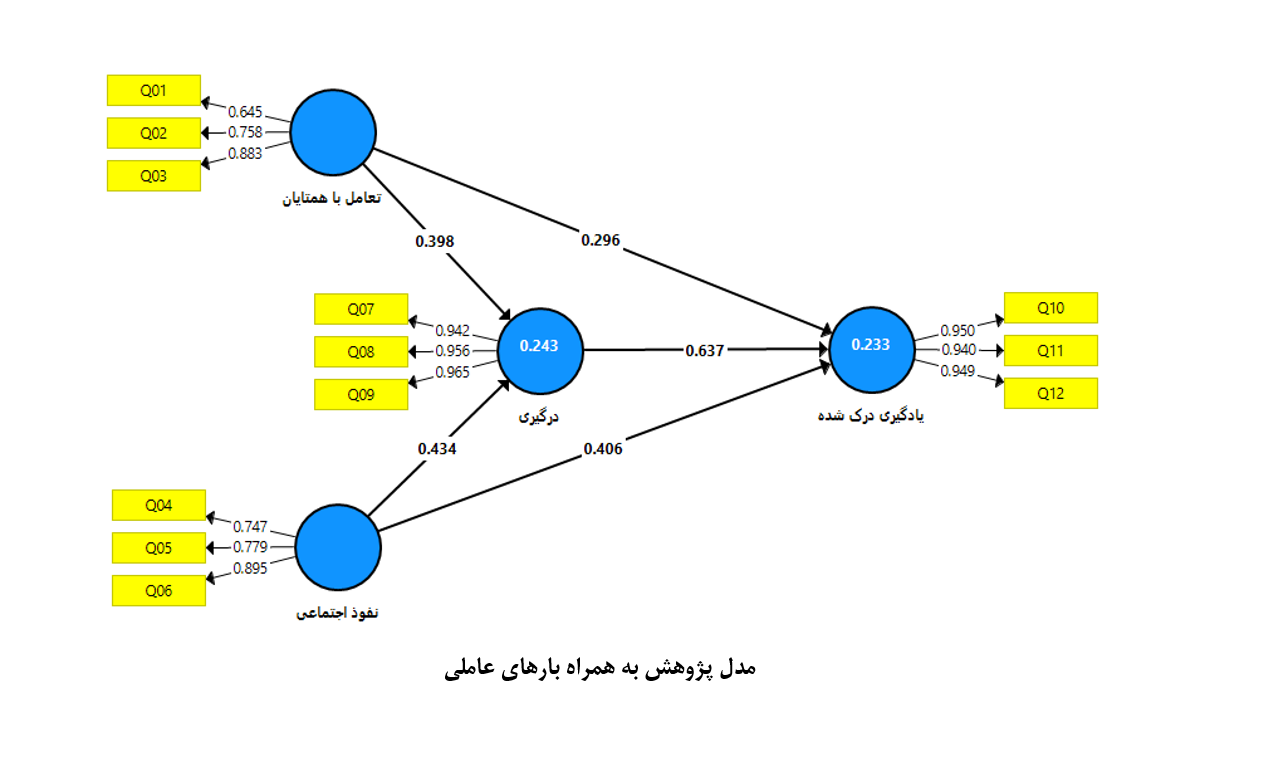
هدف پژوهش حاضر بررسی تأثیر تعامل با همتایان و نفوذ اجتماعی بر یادگیری درکشده دانشآموزان دوره ابتدایی با نقش میانجی درگیری تحصیلی است. این پژوهش از نوع توصیفی-پیمایشی و با هدف کاربردی انجام شد. جامعه آماری شامل تمامی دانشآموزان دوره ابتدایی شهرستان تنکابن بود. با استفاده از فرمول کوکران، نمونهای به حجم ۳۸۴ نفر به روش نمونهگیری تصادفی طبقهای انتخاب شد. ابزار گردآوری دادهها شامل چهار پرسشنامه معتبر برگرفته از مطالعه چانگ و پن (2023) بود که به ترتیب متغیرهای تعامل با همتایان، نفوذ اجتماعی، درگیری تحصیلی و یادگیری درکشده را در قالب مقیاس لیکرت پنجدرجهای میسنجیدند. دادهها با استفاده از نرمافزار Smart PLS و آزمون مدلسازی معادلات ساختاری تحلیل شدند. نتایج نشان داد که تعامل با همتایان و نفوذ اجتماعی هر دو تأثیر مثبت و معناداری بر یادگیری درکشده دارند. همچنین، درگیری تحصیلی بهعنوان متغیر میانجی، نقش تقویتکنندهای در رابطه بین تعاملات اجتماعی و یادگیری ایفا کرد. ضرایب مسیر، آمارههای t و نتایج بوتاسترپ نشان داد که مدل پیشنهادی از برازش مطلوبی برخوردار است. یافتهها تأکید میکنند که کیفیت روابط اجتماعی دانشآموزان و احساس تعلق و درگیری در فرآیند یادگیری نقش تعیینکنندهای در بهبود یادگیری ادراکشده دارد. طراحی محیطهای آموزشی مبتنی بر تعامل و حمایت اجتماعی میتواند موجب ارتقاء نتایج تحصیلی شود.
دانلودها
مراجع
La Greca AM, Lopez N. Peer relations, friendships, and romantic relationships: Implications for social anxiety. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology. 2022;49(1):20-35. doi: 10.1207/s15374424jccp3401_5.
Taylor HG, Hoskinson KR, Vrantsidis DM, Minich N, Busch T, Horn T, et al. Quality of Social Relationships With Parents and Peers in Adolescents Born Extremely Preterm. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics. 2023;44(3):e218-e24. doi: 10.1097/dbp.0000000000001165.
Karna W, Stefaniuk I. The Influence of Peer Relationships on the Social Development of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Iranian Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. 2024;2(4):10-8. doi: 10.61838/kman.jndd.2.4.2.
Yang L, Lian LH. Perceive Social Support, Academic Self-Efficacy, and Learning Engagement Among High School Students in China. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (Ijere). 2025;14(1):629. doi: 10.11591/ijere.v14i1.31029.
Moradi S, Mardani F. The Impact of Peer Attachment on Academic Motivation: A Quantitative Analysis. KMAN Counseling & Psychology Nexus. 2023;1(2):4-9. doi: 10.61838/kman.psychnexus.1.2.2.
Fink E, Rosnay Md. Examining Links Between Affective Empathy, Cognitive Empathy, and Peer Relationships at the Transition to School. Social Development. 2023. doi: 10.1111/sode.12685.
Öztop F, Bilač S, Kutuk Y. Improving Empathy and Peer Relationships in Adolescents: A Social Cognition Training Approach. International Journal of Education and Cognitive Sciences. 2024;5(2):23-30. doi: 10.61838/kman.ijeas.5.2.4.
Giovazolias T. The Relationship of Rejection Sensitivity to Depressive Symptoms in Adolescence: The Indirect Effect of Perceived Social Acceptance by Peers. Behavioral Sciences. 2023;14(1):10. doi: 10.3390/bs14010010.
Junaid S, Batool SS, Nazir R, Nayyar A. Relationship Between Peer Pressure and Risk Taking Behavior Among Adolescents: Moderating Role of Family Functioning. Res J Social Affairs. 2025;3(1):121-8. doi: 10.71317/rjsa.003.01.0056.
Kim H, Barry CT. Social intelligence as moderator in the relation between narcissism and aggression in at-risk adolescents. Social Development. 2023;32(2):740-55.
Lim J, Huh Z. Relationship Between Parental Monitoring and Cyberbullying Perpetration Among Male and Female Adolescents: Dual Sequential Mediating Effects of Self-Control and Peer Conformity of Anti-Social Behaviors. Korea University Institute of Educational Research. 2024;91:139-65. doi: 10.24299/kier.2024.372.139.
Xie J, Zhang B, Yao Z, Peng B, Chen H, Juan G. The Relationship Between Social Mobility Belief and Learning Engagement in Adolescents: The Role of Achievement Goal Orientation and Psychological Capital. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022;13. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.792108.
Zhang F, Peng W. Parental Psychological Control and Children's Learning Engagement and Life Satisfaction: The Moderating Role of Perceived Social Mobility. Psychology in the Schools. 2025;62(5):1422-33. doi: 10.1002/pits.23407.
Suwajo T. Correlation of Learning Engagement and Social Support Affecting the Academic Stress of Thai High School Students. International Journal of Public Health Science (Ijphs). 2024;13(3):1095. doi: 10.11591/ijphs.v13i3.23680.
Zhou X. The Effect of Peer Relationships on College Students’ Behavioral Intentions to Be Physically Active: The Chain-Mediated Role of Social Support and Exercise Self-Efficacy. Plos One. 2025;20(5):e0320845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320845.
Wang R, Ramel MRM. Social Support and Mathematics Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Learning Engagement. Social Behavior and Personality an International Journal. 2023;51(9):1-9. doi: 10.2224/sbp.12572.
Liwanag MF, Galicia LS. Technological Self-efficacy, Learning Motivation, and Selfdirected Learning of Selected Senior High School Students in a Blended Learning Environment. Technium Social Sciences Journal. 2023;44(1):534-59. doi: 10.47577/tssj.v44i1.8980.
Marsus Nb, Huey LS, Saffari N, Motevalli S. Peer Relationship Difficulties Among Children With Adhd: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences. 2022;12(6). doi: 10.6007/ijarbss/v12-i6/13352.
Mobarez M. Social and Emotional Learning in E-Lectures and Its Relation to Academic Achievement, Social Isolation and Engagement in Learning Among Graduate Students. Ijre. 2023;47(3):203-40. doi: 10.36771/ijre.47.3.23-pp203-240.
Slåtten T, Lien G, Batt-Rawden VH, Evenstad SBN, Onshus T. The relationship between students’ psychological capital, social-contextual factors and study-related outcomes – an empirical study from higher education in Norway. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences. 2023;15(1):17-33. doi: 10.1108/IJQSS-11-2021-0160.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Narges Amir Janati (Author); Samira Pali (Corresponding author)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










