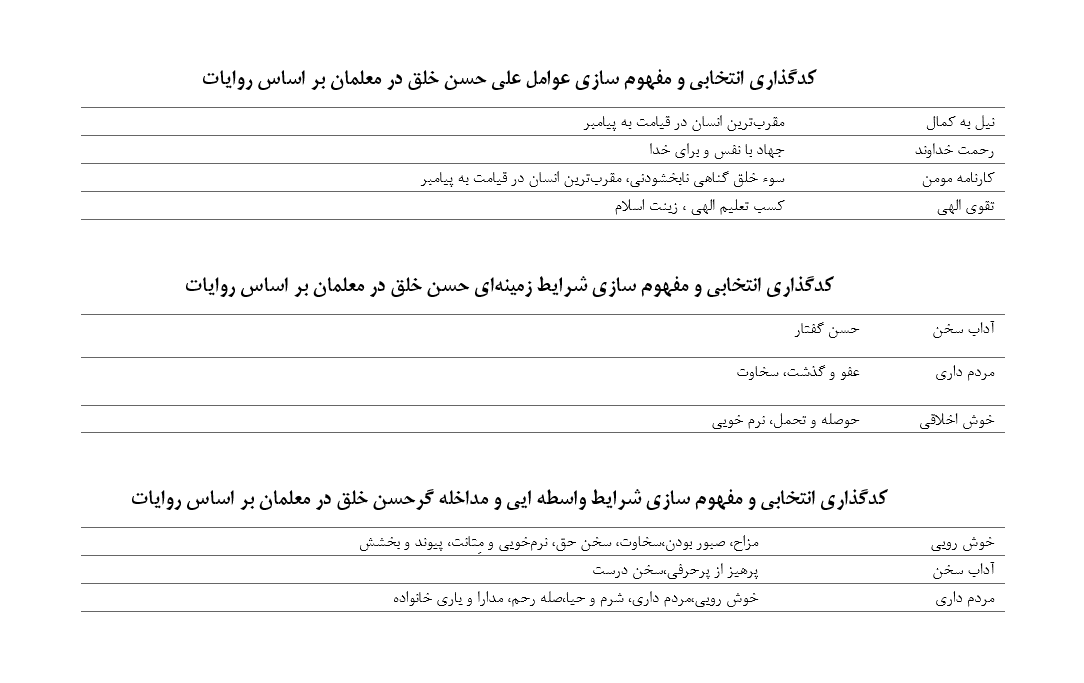
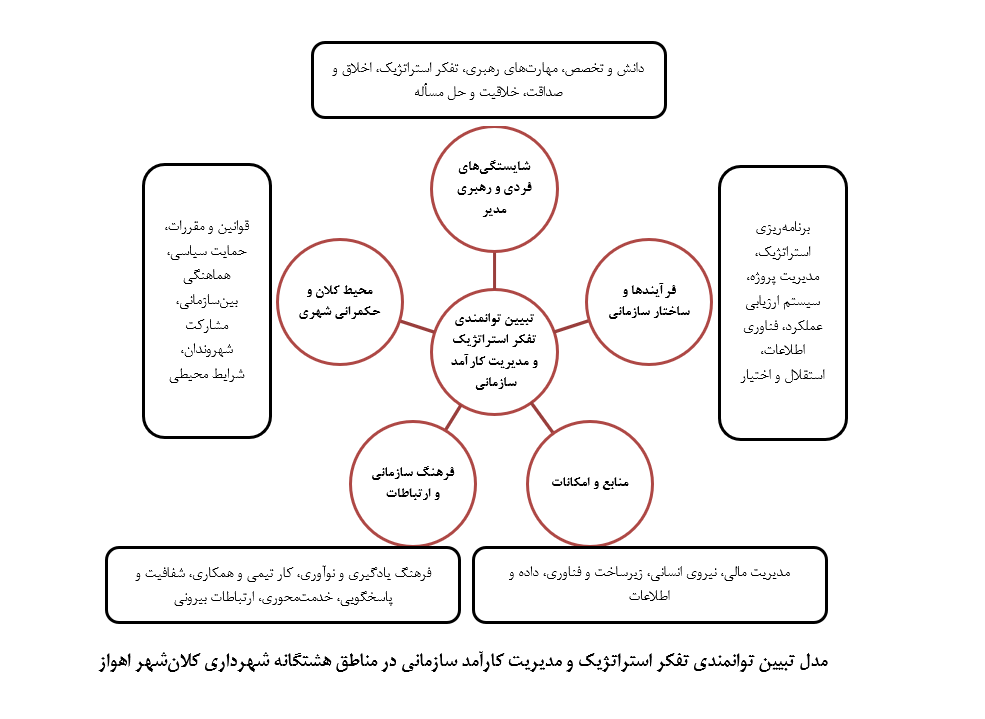
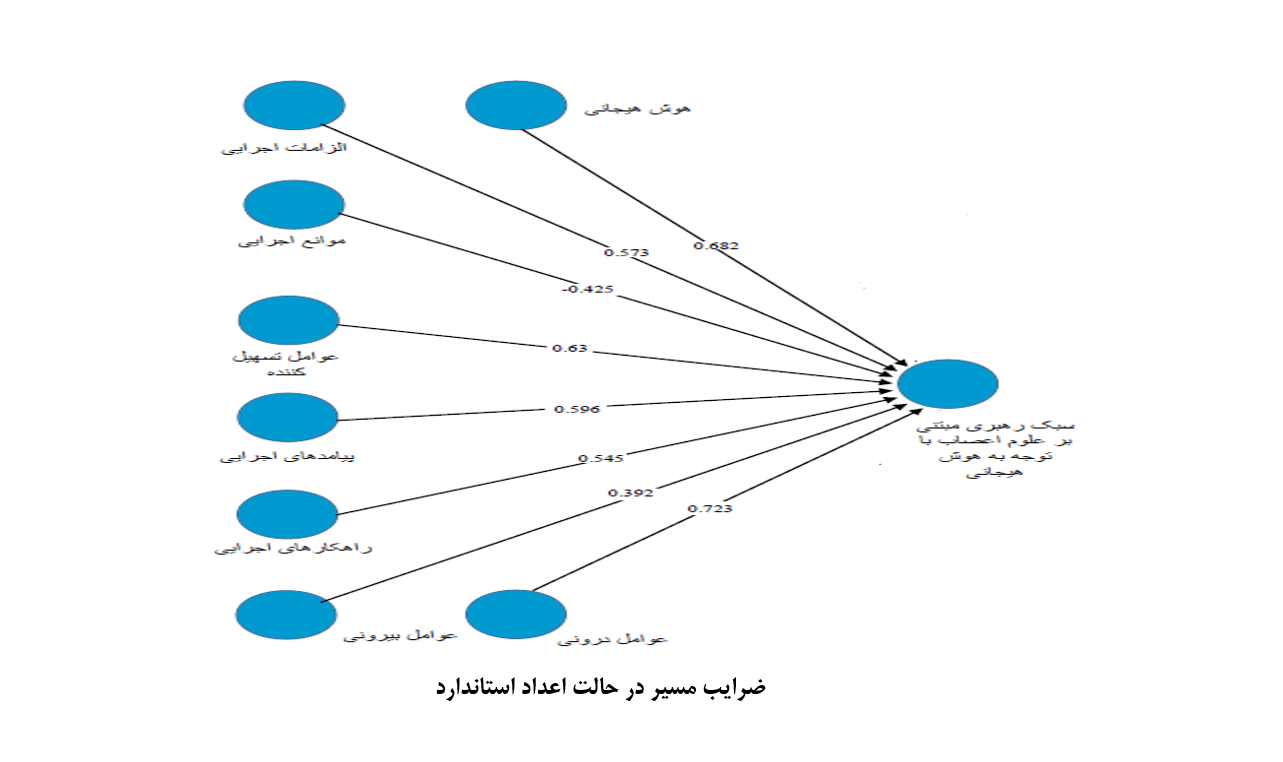
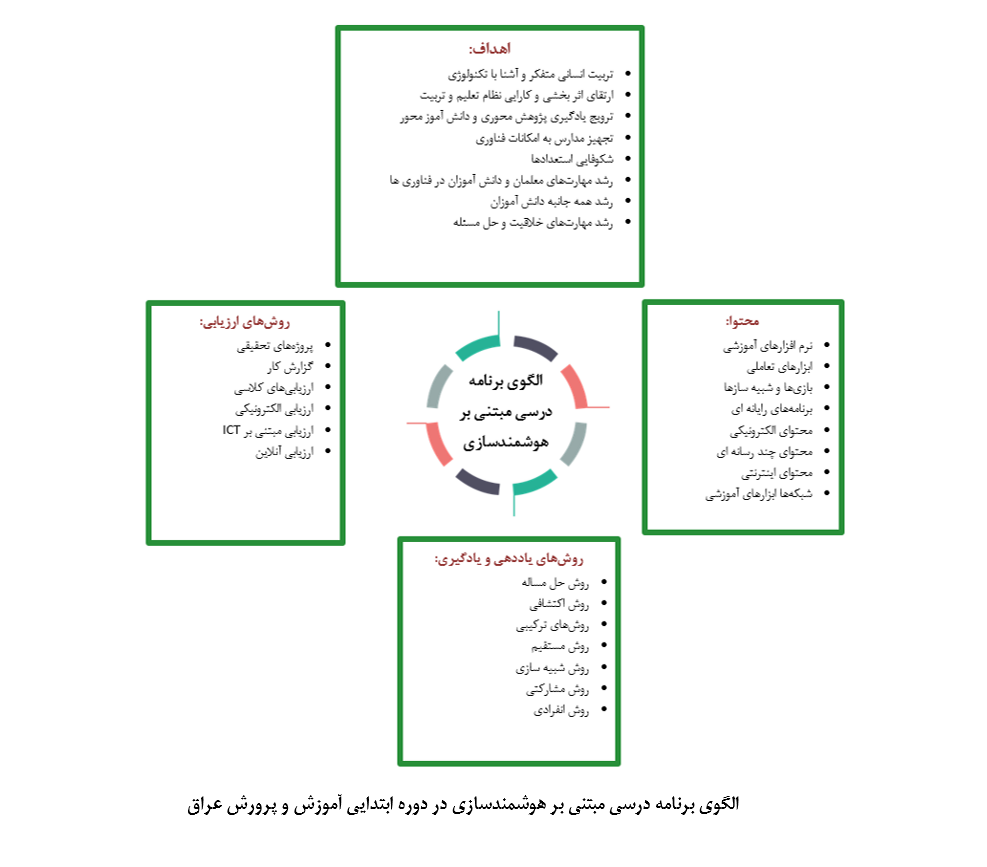
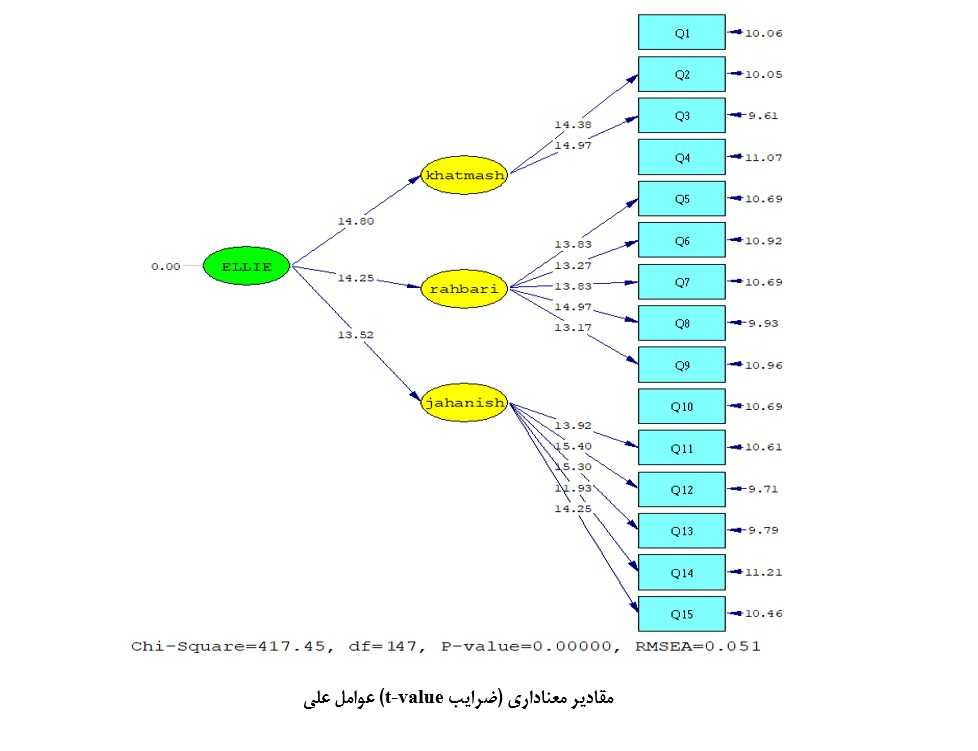
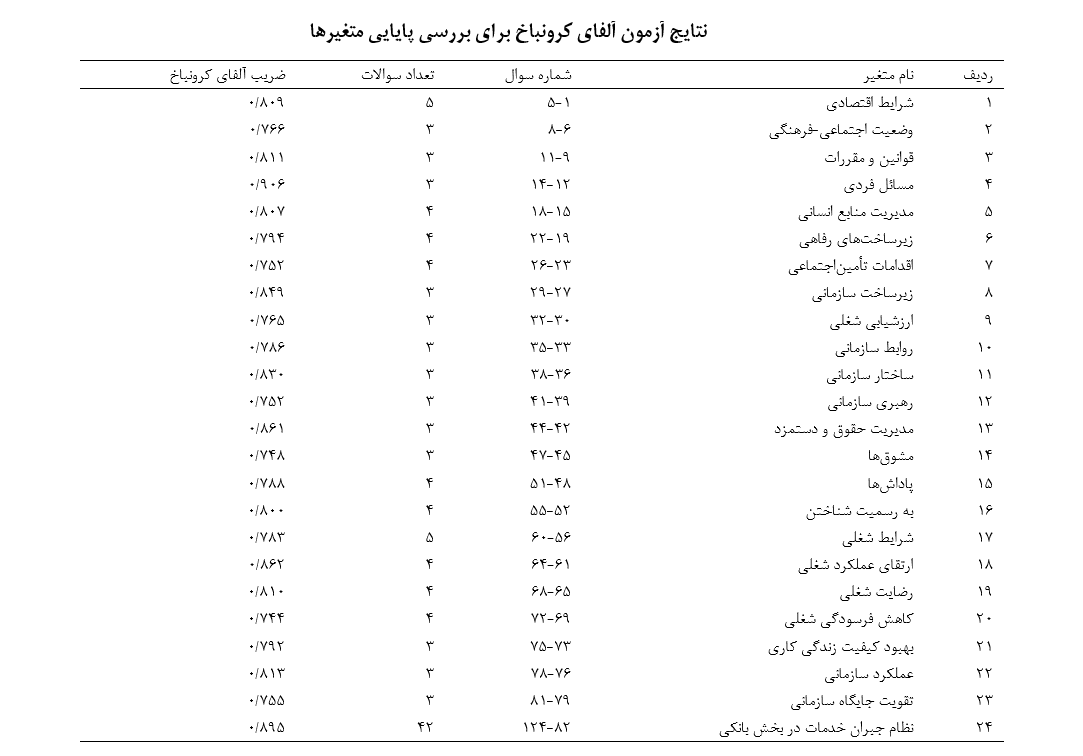
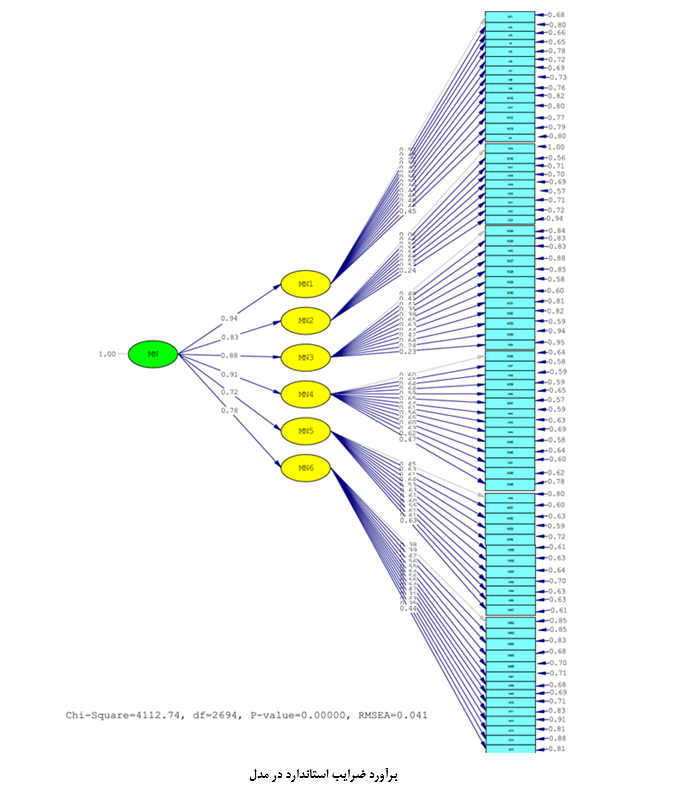
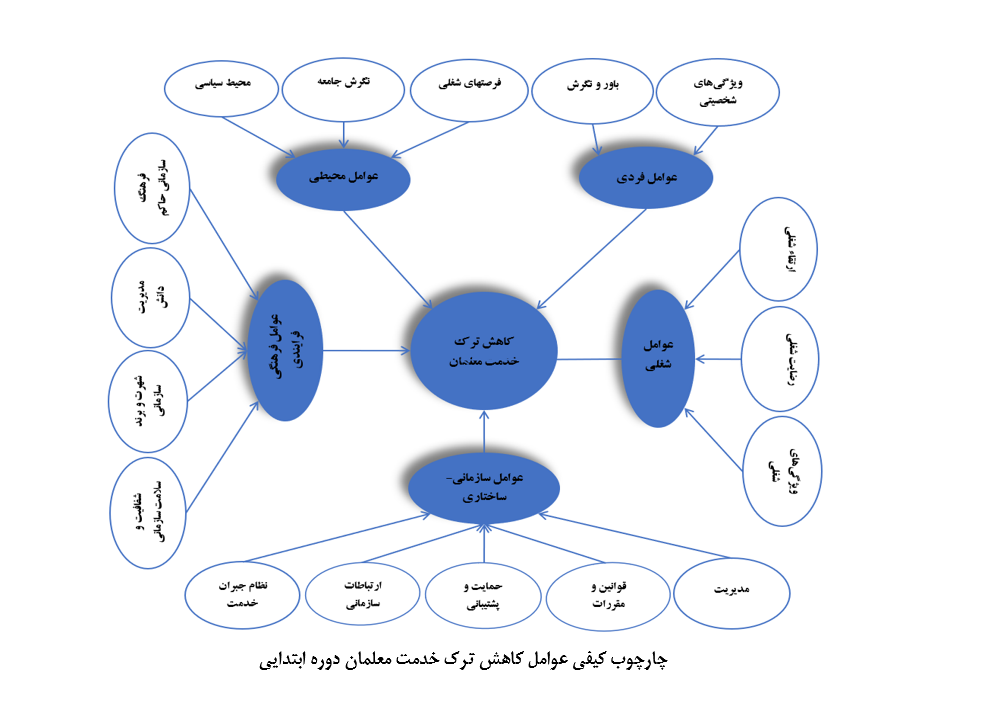
About the Journal
The Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development (JSIED) is a leading international, open-access journal that serves as a vital forum for the dissemination of research and advancements in the fields of education and development. Our journal is dedicated to promoting scholarly excellence by publishing high-quality, original research articles, comprehensive reviews, case studies, and theoretical papers that contribute to the understanding and improvement of educational practices and developmental theories globally.
JSIED stands at the intersection of innovation, education, and development, aiming to bridge the gap between theoretical research and practical applications. We encourage submissions from a diverse array of disciplines, including but not limited to, pedagogy, educational psychology, instructional design, curriculum development, educational technology, and international development. Our journal is designed to serve as a critical resource for educators, researchers, policymakers, and practitioners who seek to advance knowledge and foster innovation in education and development.