مقایسه اثر بخشی آموزش درگیری شناختی با آموزش راهبردهای فراشناخت بر اهمال کاری تحصیلی دانشجویان دختر دانشگاه فرهنگیان
کلمات کلیدی:
درگیری شناختی, فراشناخت, آموزش راهبردی, همال کاری تحصیلیچکیده
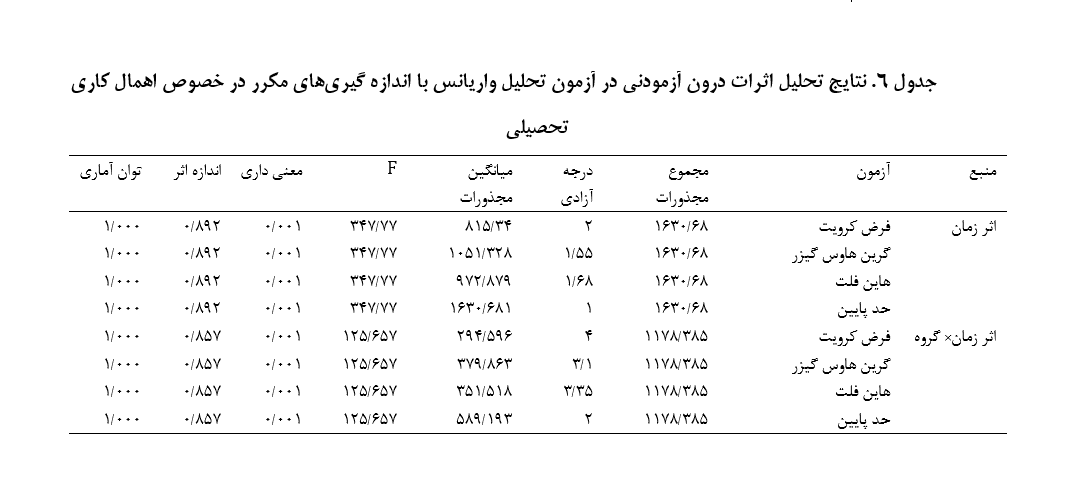
این پژوهش با بررسی تفاوت بین اثربخشی بسته آموزشی درگیری شناختی و بسته آموزشهای فراشناخت بر اهمال کاری تحصیلی دانشجویان دختر دانشگاه فرهنگیان انجام شد. روش پژوهش نیمه آزمایشی وطرح آن از نوع پیش آزمون-پس آزمون با گروه کنترل و دوره پیگیری دو ماهه بود. جامعه آماری پژوهش حاضر در قسمت کمی شامل کلیه دانشجویان دختر دانشگاه فرهنگیان کازرون نیم سال اول 1399-1398 بودند که تعداد این افراد 250 نفر بود. روش نمونه گیری جهت مقایسه بسته درگیری شناختی و راهبردهای فراشناختی به صورت هدفمند ابتدا پرسش نامه اهمالکاری تحصیلی (سواری، 1390) روی 250 نفراز دانشجویان دختر دانشگاه فرهنگیان کازرون اجرا شد. و از بین کسانی که در اهمالکاری تحصیلی نمره تا 48 به دست آوردند،تعداد 45 نفر به شیوه هدفمند انتخاب و به صورت تصادفی در دو گروه آزمایش (درگیری شناختی15 نفر- راهبرد فراشناخت 15 نفر) و گروه کنترل 15 نفرگمارده شدندِ. در مرحله پس آزمون و پیگیری بین میانگین نمرات اهمال کاری تحصیلی در گروه کنترل با گروه آموزش فراشناخت(001/0p<) و بسته آموزش درگیری شناختی (01/0p<) تفاوت معنی داری وجود دارد که نشان میدهد میزان تأثیر آموزش فراشناخت بر کاهش اهمال کاری تحصیلی در پس آزمون و پیگیری به ترتیب برابر با 5/33 و 1/28 درصد حاصل شده است. تأثیر بسته آموزش درگیری شناختی در کاهش اهمال کاری تحصیلی در پس آزمون و پیگیری به ترتیب برابر با 9/69 و 66 درصد حاصل شده است. ضمن معنی داری اثرات هر د وروش آموزشی درگیری شناختی و فراشناخت در کاهش اهمال کاری تحصیلی در مرحله پس آزمون، در هر دو روش آموزشی اهمال کاری تحصیلی در مرحله پیگیری افزایش داشته است، و در مقایسه دو روش آموزشی نیز، در هر دو مرحله پس آزمون و پیگیری، روش آموزشی درگیری شناختی اثربخش تر از آموزش فراشناخت بوده است.
دانلودها
مراجع
Joojam P, Safarpour-Dehkordi S. The Effect of Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies on Self-Concept and
Academic Procrastination in Middle School Students. Excellence in Education Quarterly. 2024;3(2):6-10.
Pintrich P. The role of motivation in promoting and sustaining self-regulated learning. International Journal of
Educational Research. 2003;31:450-70. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(99)00015-4.
Jabbari Daneshvar A, Rezayi A. The Role of Academic Identity and Goal Orientation in Predicting Cognitive
Engagement of Students. Advances in Behavioral Sciences. 2023;7(55):478-91.
Torabi K, Nikookar A. The Role of Academic Engagement Dimensions and Responsibility in Academic Self-Efficacy
of 8th Grade Female Students. School Counseling. 2021;1(2):1-16.
Najarian Z, Vahedi S. The Relationship of Perseverance, Psychological Hardiness, and Resilience With Academic
Engagement in Students: A Path Analysis Model. Educational Psychology Quarterly. 2023;18(66):169-92.
Karimi SB, Mehrparvar M. The Effectiveness of Training Cognitive and Metacognitive Learning Strategies on
Reflective Thinking and Self-Directed Learning in Students. Learner-Centered Curriculum and Education Journal. 2021;1(4).
Saif AA. New Educational Psychology. Tehran: Douran Publishing; 2016.
Lotf Abadi H. Educational Psychology. Tehran: SAMT Publishing; 2005.
Faraji S. Explaining the Relationship Between Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies With Cognitive Engagement
in High School Students in Ilam. Ilam: Bakhtar Institute of Higher Education; 2021.
Pour Abdol S, Sobhi Gharamaki N, Abbasi M. Comparison of Academic Procrastination and Academic Vitality in
Students With and Without Specific Learning Disabilities. Learning Disabilities Journal. 2015;3(4):22-38.
Sheikholeslami A. The Effectiveness of Training Cognitive and Metacognitive Learning Strategies on Academic
Procrastination in Students With Low Academic Achievement. School Psychology Journal. 2017;6(3):65-84.
Mesrabadi J, Erfani Abab E. Meta-analysis of the relationship between learning strategies and academic achievement.
Biquarterly Journal of Cognitive Strategies in Learning. 2014;2(2):97-118.
Babaei S, editor The Relationship Between Academic Procrastination and Personality Traits of Students. First
National Conference on Sustainable Development in Educational and Psychological Sciences; 2017.
Amir Ardejani N. The Effect of Training Metacognitive Strategies on Locus of Control and Flow Experience in
Female High School Students. Rooyesh Psychology Journal. 2023;11(7):189-98.
Ghadampour E, Biranvand K. The Effect of Cognitive and Metacognitive Learning Strategies Training on Academic
Procrastination and Self-Efficacy of Students. Cognitive Sciences Quarterly. 2019;21(3):31-41. doi: 10.30699/icss.21.3.31.
Taghaviania A. The Effect of Metacognitive Strategy Training on Help-Seeking and Academic Procrastination in
Conditional Students. Cognitive Strategies in Learning Biannual. 2018;6(11):193-214.
Nemat Zadeh Souteh G, Ghanadzadegan, Emadian SA. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral
Training Based on Procrastination and Multidimensional Motivational Cognitive Intervention on Academic Procrastination in
High School Students With Addicted Parents. Social Psychology Research. 2024;13(49):77-90.
Jafari L, Bigdeli K. The Relationship Between Self-Regulation (Cognitive and Metacognitive) and Academic
Procrastination With Adaptation to Goals in Islamic Azad University Students. Analytical Cognitive Psychology Quarterly.
;13(51):15-32.
Zhou M, Lam KKL, Zhang Y. Metacognition and academic procrastination: A meta-analytical examination. Journal
of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy. 2022;40(2):334-68. doi: 10.1007/s10942-021-00415-1.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2024 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










