مدل مفهومی مدیریت اوتیسم اجتماعی در سازمانهای دولتی ایران: رویکردی برآمده از تحلیل مضمون
کلمات کلیدی:
اوتیسم اجتماعی, سازمانهای دولتی, مدیریت, مدل مفهومی, تحلیل مضمونچکیده
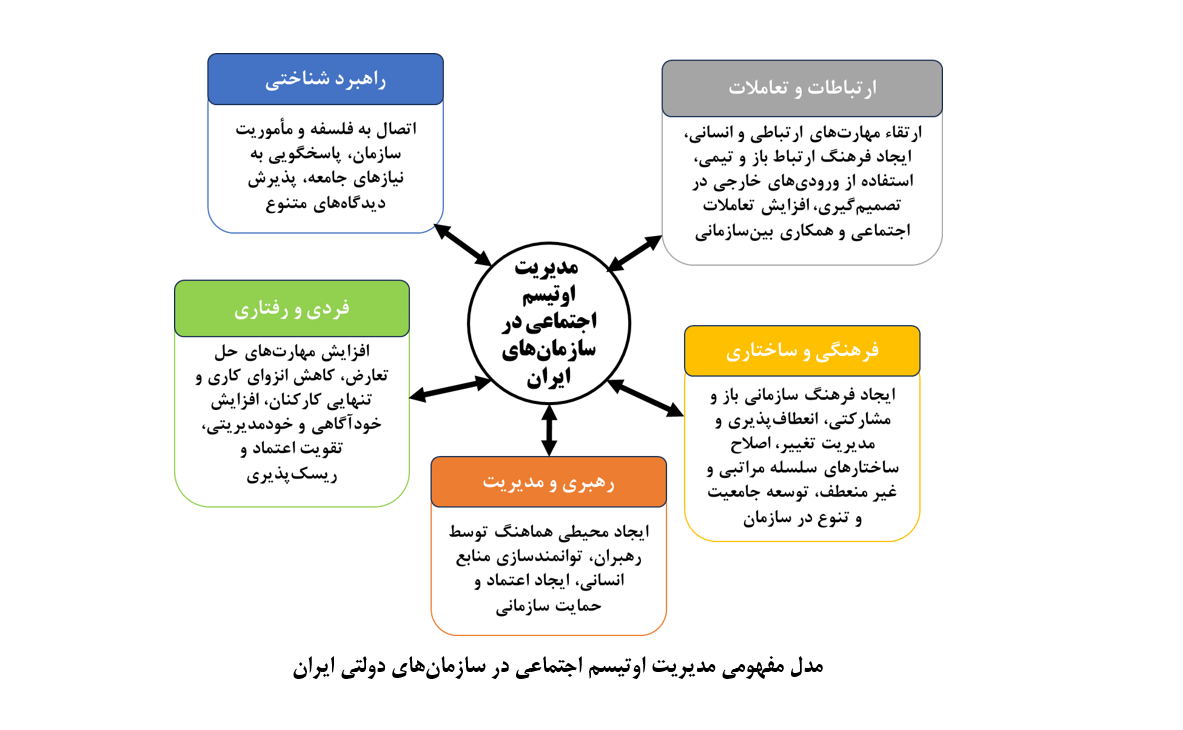
هدف این پژوهش ارائه مدل مفهومی مدیریت اوتیسم اجتماعی در سازمانهای دولتی ایران، به روش کیفی و مبتنی بر تحلیل مضمون است. جامعه آماری پژوهش شامل متخصصین دانشگاهی، متخصصین اجرایی سازمانهای دولتی، روانشناسان سازمانی، پژوهشگران حوزه اوتیسم و سایر صاحبنظران مرتبط با مدیریت اوتیسم اجتماعی در محیط کار دولتی بود. نمونهگیری به صورت ترکیبی از روشهای هدفمند (قضاوتی) و گلولهبرفی انجام شد و با 17 مصاحبه نیمهساختاریافته به اشباع مضمونی رسید. دادهها از طریق مصاحبههای عمیق نیمهساختاریافته جمعآوری و با استفاده از روش تحلیل مضمون بر اساس مراحل ششگانه براون و کلارک (2006) تحلیل شدند. برای اطمینان از روایی پژوهش، معیارهای اعتبار (مقبولیت)، انتقالپذیری، تأییدپذیری و قابلیت اطمینان بررسی و تأیید شدند و درصد توافق دو کدگذار 81% گزارش شد که نشاندهنده پایایی بالای تحلیل است. نتایج تحلیل مضمون 151 عبارت معنایی را در 62 کد باز و نهایتاً در 18 کد محوری و 5 بعد اصلی دستهبندی کرد. این پنج بعد شامل «راهبردی و شناختی»، «ارتباطات و تعاملات»، «فرهنگی و ساختاری»، «رهبری و مدیریت» و «فردی و رفتاری» میباشند. این پژوهش با ارائه یک مدل مفهومی یکپارچه و عملیاتی، به چالشهای معاصر اوتیسم اجتماعی در سازمانهای دولتی پاسخ میدهد و میتواند راهنمایی برای سیاستگذاری و ترویج محیطهای کاری فراگیر باشد. نوآوری این پژوهش در ارائه اولین مدل مفهومی بومیسازی شده برای مدیریت اوتیسم اجتماعی در سازمانهای دولتی ایران نهفته است.
دانلودها
مراجع
Parsons BM, Pinzone M, Albè F, Orlandelli D, Barletta I, Berlin C, et al. Local autism policy networks: Expertise and intermediary organizations A framework for operative and social sustainability functionalities in Human-Centric Cyber-Physical Production Systems. Educational Policy. 2018;32(6):823-54. doi: 10.1177/0895904816673743 10.1016/j.cie.2018.03.028.
Kester JS, Hill T, Thompson L, Black CL, Coriano VL, Bruton J, et al. Variance in Autism Prevalence: Links with State-Level Autism Resources. Journal of Disability Policy Studies. 2023:10442073231156940. doi: 10.1177/10442073231156940.
Georgeac OA, Rattan A. The business case for diversity backfires: Detrimental effects of organizations' instrumental diversity rhetoric for underrepresented group members' sense of belonging. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2023;124(1):69. doi: 10.1037/pspi0000394.
Sajjad A, Shahbaz W. Mindfulness and social sustainability: An integrative review. Social Indicators Research. 2020;150(1):73-94. doi: 10.1007/s11205-020-02297-9.
Farzaneh A, Seddigh Orouei G, Bagheri M. Empirical Typology of Social Interaction Problems in the Neighborhood Relationship Network (Research Case: Mashhad City). Journal of Iranian Social Studies. 2023;17(3):153-85.
Deutschmann JW, Lipscomb M, Schechter L, Zhu J. Spillovers without social interactions in urban sanitation. American Economic Journal: Applied Economics. 2024;16(3):482-515. doi: 10.1257/app.20220047.
Chuang S. Indispensable skills for human employees in the age of robots and AI. European Journal of Training and Development. 2022. doi: 10.1108/EJTD-06-2022-0062.
Shamsi S, Pourateshi M, Zamani A. Investigating the Relationship Between Managers' Communication Skills and Leadership Style with Human Resource Empowerment: A Case Study of Dr. Shariati Technical College. Karafan Scientific Quarterly. 2019;16(2):141-60.
Kaplan LR, Farooque M, Sarewitz D, Tomblin D. Designing participatory technology assessments: a reflexive method for advancing the public role in science policy decision-making. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 2021;171:120974. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120974.
Waldman DA, Sparr JL. Rethinking diversity strategies: An application of paradox and positive organization behavior theories. Academy of Management Perspectives. 2023;37(2):174EP - 92. doi: 10.5465/amp.2021.0183.
Rasool SF, Wang M, Tang M, Saeed A, Iqbal J. What a toxic workplace environment effects the employee engagement: The mediating role of organizational support and employee wellbeing. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2021;18(5):2294. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052294.
Goldhaber GM. Organizational communication1993.
Sumaiya B, Srivastava S, Jain V, Prakash V. The Role of Effective Communication Skills in Professional Life. World Journal of English Language. 2022;12(3):134-40. doi: 10.5430/wjel.v12n3p134.
John-Eke EC, Akintokunbo OO. Conflict management as a tool for increasing organizational effectiveness: A review of literature. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences. 2020;10(5):299-311. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v10-i5/7198ER -.
Boikanyo DH, Naidoo M. The influence of organisational support, advancement, meaningfulness and psychological safety on employee engagement in a petrochemical organisation. WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS. 2023;20:1100-9. doi: 10.37394/23207.2023.20.98.
Shore LM, Cleveland JN, Sanchez D. Inclusive workplaces: A review and model. Human Resource Management Review. 2018;28(2):176-89. doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2017.07.003.
Nishii LH. The benefits of climate for inclusion for gender-diverse groups. Academy of Management journal. 2013;56(6):1754-74. doi: 10.5465/amj.2009.0823.
Georgakopoulos A, Allen B, Petzold-Bradley E. Managing Organizational Conflicts Through Innovation, Creativity, and Inclusion: Implementing a Conflict System of Shared Leadership. De Gruyter Handbook of Organizational Conflict Management2022. p. 233.
Da Rocha JPP, Frazier EB. Conflict, Systems, and Approaches to Conflict Management: An Overview. Strategic Approaches for Conflict Resolution in Organizations: Emerging Research and Opportunities2020. p. 1-30.
Nguyen TD. Resolving conflict in organizations-achieving results through a harmonization process. Development and Learning in Organizations: An International Journal. 2019;33(5):4-7. doi: 10.1108/DLO-10-2018-0136.
Vandergoot S, Sarris A, Kirby N. Factors That Influence the Training Transfer and Maintenance of Conflict Resolution Programs of Healthcare Training and Development Units: A Retrospective Study. Applied Psychology Readings: Selected Papers from Singapore Conference on Applied Psychology, 20172018. p. 103-21.
Hartmann CW, Engle RL, Pimentel CB, Mills WL, Clark VA, Keleher VC. Virtual external implementation facilitation: Successful methods for remotely engaging groups in quality improvement. Implementation science communications. 2021;2(1):1-10. doi: 10.1186/s43058-021-00168-z.
Cwinn E, Barry EA, Weisz JR, Bailin A, Fitzpatrick OM, Venturo-Conerly K, et al. Brief digital interventions: An implementation-sensitive approach to addressing school mental health needs of youth with mild and emerging mental health difficulties. Canadian Journal of Community Mental Health. 2022;41(3):157-75. doi: 10.7870/cjcmh-2022-026.
Kotter JP. Leading change: Harvard business press; 2012.
Northouse PG. Leadership: Theory and practice: Sage publications; 2021.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Naghmeh Keyhanian (Author); Mehran Mokhtari Bayekolaei (Corresponding author); Davood Kia Kojouri (Author)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










