Identifying Influential Components in Competency-Based Curriculum for Physical Education Student Teachers
Keywords:
curriculum, teacher competency, physical education student teachers, qualitative analysisAbstract
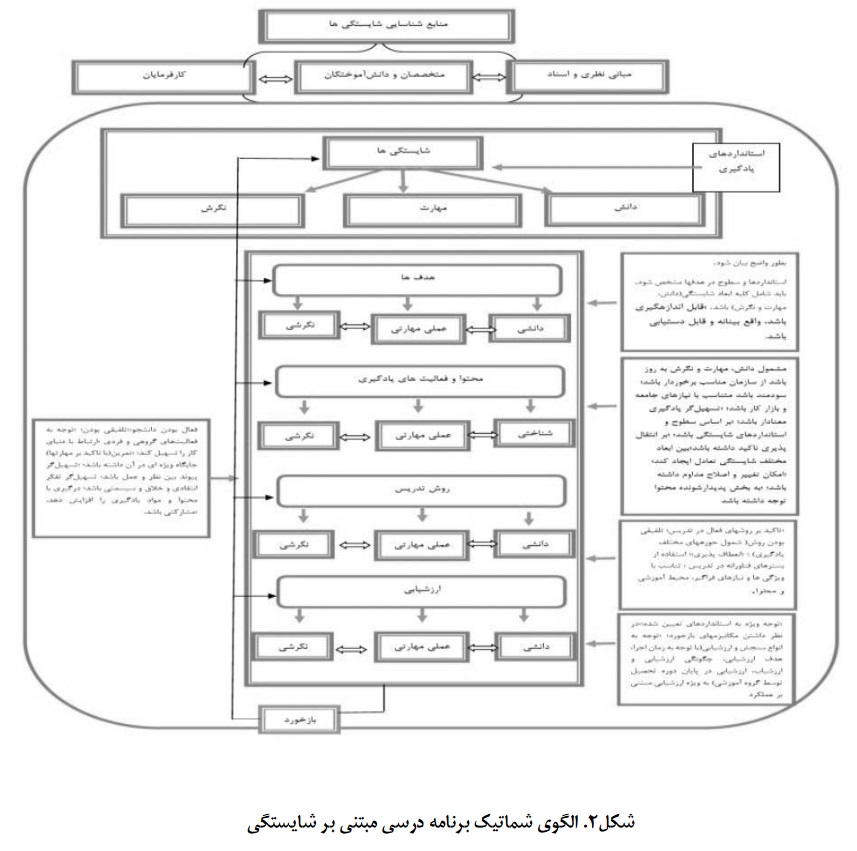
The aim of the present study is to identify the influential components in a competency-based curriculum for physical education student teachers. This research is applied in nature and utilizes a qualitative methodology. A document analysis method was primarily used to develop a conceptual matrix aimed at identifying competencies, characteristics, and examples of curriculum elements based on competencies. The statistical population consists of five groups: (1) academic experts in curriculum planning, (2) employers, (3) graduates of physical education teacher training programs from universities, (4) domestic documents related to the field of physical education teacher training, and (5) domestic and international scientific sources and research published on competency-based curriculum. To identify the competencies of physical education student teachers and to design a competency-based curriculum model, semi-structured individual interviews were conducted until theoretical saturation was achieved. The results indicated that the expected competencies for physical education student teachers are classified into three themes and seven categories. The findings of this research were categorized into the following themes: cognitive competencies (with three categories: specialized knowledge in physical education, general cognitive competencies, and general knowledge), skill-based competencies (with two categories: specialized physical education curriculum skills and general skills), and attitudinal and emotional competencies (with two categories: attitudinal competencies related to the physical education curriculum and general attitudinal competencies). The elements and characteristics of competency-based curriculum components for physical education student teachers include objectives, content, learning activities, methods, and evaluation.
Downloads
References
Wang D. Research on Intelligent Curriculum Teaching for Art and Design Majors in Colleges and Universities in the
Information Age. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences. 2024;9(1). doi: 10.2478/amns-2024-0266.
Lee I, Perret B. Preparing High School Teachers to Integrate AI Methods into STEM Classrooms. Proceedings of the
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2022;36(11):12783-91. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i11.21557.
He N. The Study on the Curriculum of Elementary School Under the Worldwide Curriculum System. Creative
Education. 2023;14(03):429-35. doi: 10.4236/ce.2023.143028.
Hosseini Largani SM. The Analysis of Curriculum Development in Iran†™s Higher Education. Quarterly Journal of
Research and Planning in Higher Education. 2023;26(4):1-28.
Moon YL. Education Reform and Competency Based Education. Asia Pacific Education Review. 2007. doi:
1007/BF03029267.
Rodriguez BF, Figueroa-Sandoval B, Figueroa KA. Competence training in higher education: the case of the
technological master "Prestación De ServiciosProfesionales" fromTheColegio De Postgraduados (Mexico). Procedia - Social
and Behavioral Sciences. 2012;46:2389-94. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.490.
Abdoli Sajzi A, Talai M, editors. Competency-based curriculum in higher education. The first international conference
on psychology, social sciences and humanities; 2019.
Rahnama Zarbijari B, editor Curriculum design based on the competency document for the master's course in the
curriculum field. The first international conference of educational sciences, psychology and humanities; 2021.
Arefi M. Strategic curriculum planning in higher education. Tehran: Shahid Beheshti University Press; 2004.
Mohammadi M, Dehdari Rad T. Evaluation of the core competence of the curriculum of the automotive mechanics
associate course. Iranian Curriculum Studies Quarterly. 2009;5(19):43-64.
Momeni Mehmoi H, Kazempour I, Tafarshi M, editors. Competency-based curriculum planning, a desirable strategy
for the development of basic competence2010.
Hernández-Pina F, Monroy F. A preliminary study of teachers' perception of core competencies for undergraduate
students. Psicología educativa. 2015;21(1):11-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pse.2015.02.001.
Yousefi Afrashteh M, Ghazi Tabatabai M, Gharavi MJ, Bazargan A, Shakohi Yakta M. Expected learning
achievements of laboratory science graduates from the point of view of employers: a qualitative research. Journal of Qualitative
Research in Health Sciences. 2014.
Moradi R, Moradi M, Molki H, Abdali A. Designing and presenting a competency model for curriculum planners.
Qualitative Research in Cultural Studies Curriculum. 2015.
Ryan S. Development of a competency-based curriculum in the active management of the third stage of labor for
skilled birth attendants [Doctoral Dissertation]: The Ohio State University; 2011.
Lenburg C. The framework, concepts and methods of the competency outcomes and performance assessment (COPA)
model. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing. 1999;4(2). doi: 10.3912/OJIN.Vol4No02Man02.
Lenburg CB, Abdur-Rahman VZ, Spencer TS, Boyer SA, Klein CJ. Implementing the COPA Model in Nursing
Education and Practice Settings: Promoting Competence, Quality Care, and Patient Safety. Nursing education perspectives.
;32(5):290-6. doi: 10.5480/1536-5026-32.5.290.
Dilmore T, Moore D, Bjork Z. Implementing Competency-Based Education: A Process Workbook: University of
Pittsburgh Press; 2011.
McKimm J. Curriculum design and development: School of Medicine Imperial College Centre for Educational
Development; 2007.
Porcel JM, Casademont J, Conthe P, Pinilla B, Pujol R, Purwanto S, Ardriyati W. Redisigning a Competence-based
Syllabus Of English For Information Technology: A Case Study At Unisbank. Jurnal Ilmiah Dinamika Bahasa dan Budaya.
;8(1):66-76.
Wall LA. An Exploratory Study of Teacher Empowerment and Technical Education in Kentucky [Doctoral
Dissertation]: Western Kentucky University, Bowling Green, Kentucky; 2020.
Arjun P. An evaluation of the proposed new curricula for schools in relation to Kuhn's conception of paradigms and
paradigm shifts. South African Journal of Higher Education. 1998;12(1):20-6.
Gonczi A, Hager P, Oliver L. Establishing competency-based standards in the professions. Canberra: Australian
Government Publishing Service; 1990.
Cheng MS. A competency model for Culinology graduates: Evaluation of the Research Chefs Association's Bachelor
of Science in Culinology core competencies [Graduate Thesis]: Iowa State University; 2012.
Salari P, Rastegari N. Analysing the Internship Experiences of Supervisors and Teacher-Students of Farhangian
University in Elementary Schools of Kerman. Research in Elementary Education. 2020;2(3):1-15.
Anema MG, McCoy JL. Competency based nursing education: guide to achieving outstanding learner outcomes:
Springer Publishing Company; 2009.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










