Presenting a Model for Implementing E-Learning with an Omnichannel Approach in Secondary Schools (Second Level) in Tehran
Keywords:
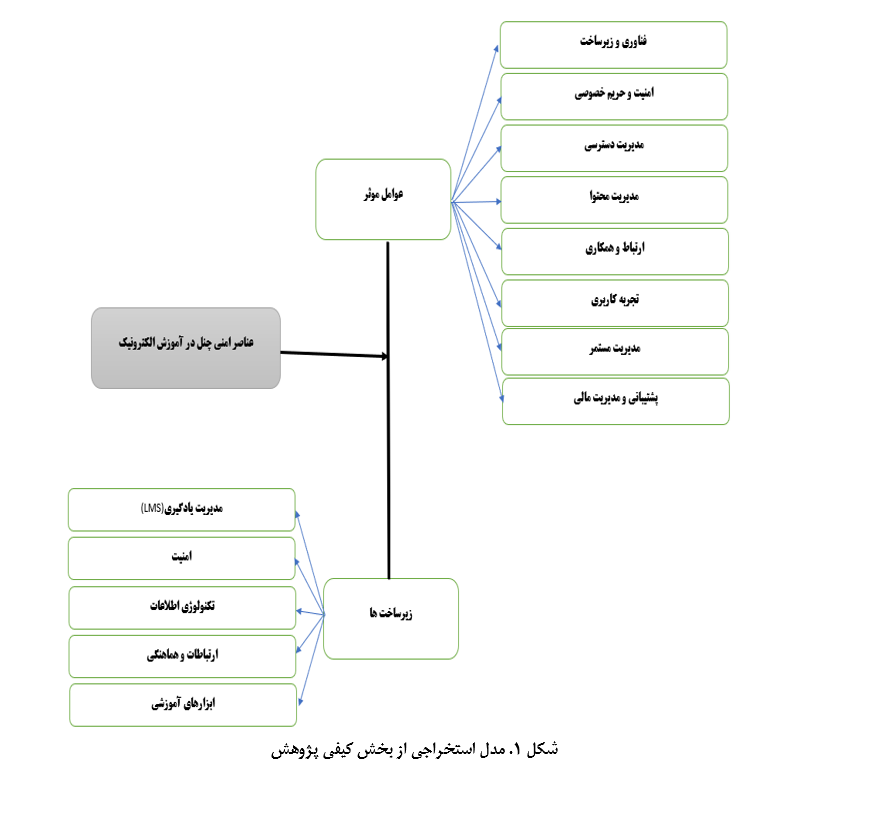
E-learning, omnichannel, technological infrastructure, secondary schools, content management , security and privacyAbstract
This study aimed to develop a model for implementing e-learning with an omnichannel approach in secondary schools (second level) in Tehran. This research adopted a mixed-methods exploratory design. In the qualitative phase, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 16 experts in e-learning and educational technology, and data were analyzed using content analysis. In the quantitative phase, a sample of 256 teachers and administrators from secondary schools (second level) was selected through stratified sampling, and a Likert-scale questionnaire was distributed among them. Quantitative data were analyzed using structural equation modeling (SEM) in AMOS software. Qualitative findings identified key themes such as technology and infrastructure, security and privacy, content management, communication and collaboration, and user experience as critical factors for successful e-learning implementation. Quantitative results confirmed that the proposed conceptual model was statistically valid, with fit indices (TLI, NFI, IFI, RMSEA, etc.) within acceptable ranges. Significant factor loadings of the core themes demonstrated strong relationships between observable indicators and latent variables. The study concluded that implementing e-learning with an omnichannel approach requires enhanced technological infrastructure, adherence to security and privacy protocols, user-friendly content and interface design, and effective collaboration among users. The proposed model offers a comprehensive framework for improving the quality of e-learning in schools.
Downloads
References
Ahmed B, Zaini S. The challenges of e-learning implementation among university students in yemen. International
Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences. 2022;12(10).
Aini Q, Budiarto M, Putra P. Exploring e-learning challenges during the global covid-19 pandemic: a review. Jurnal
Sistem Informasi. 2020;16(2):57-65.
Ali S, Uppal M, Gulliver S. A conceptual framework highlighting e-learning implementation barriers. Information
Technology and People. 2018;31(1):156-80.
Barua K, Rasania S, Acharya A, Singh A. E-learning in medical education: students’ experience, challenges and
perspectives: a cross-sectional study in india. Indian Journal of Community Health. 2021;33(4):580-5.
Bylieva D, Hong J, Lobatyuk V, Nam T. Self-regulation in e-learning environment. Education Sciences.
;11(12):785.
Lassoued Z, Alhendawi M, Bashitialshaaer R. An exploratory study of the obstacles for achieving quality in distance
learning during the covid-19 pandemic. Education Sciences. 2020;10(9):232.
Mhouti A, Erradi M. Harnessing cloud computing services for e-learning systems in higher education. International
Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education. 2019;15(2):18-30.
Maatuk A, Elberkawi E, Aljawarneh S, Rashaideh H, Alharbi H. The covid-19 pandemic and e-learning: challenges
and opportunities from the perspective of students and instructors. Journal of Computing in Higher Education. 2021;34(1):21-
Nasrat N, Khamosh A, Lavangnananda K, editors. Challenges and hurdles to e-learning implementation during covid19 outbreak: a case of shaikh zayed university2020.
Kurniawan H. Application of e-learning for online learning during the covid-19 pandemic at university of
pembangunan panca budi. Journal of Applied Engineering and Technological Science (Jaets). 2022;4(1):42-7.
Mugizi W, Rwothumio J. Universities’ capabilities and effective implementation of e-learning in public universities
in kampala city, uganda. UHERJ. 2023;10(2):68-86.
Costello J, McNaughton R. Integrating a dynamic capabilities framework into workplace e‐learning process
evaluations. Knowledge and Process Management. 2018;25(2):108-25.
Reis FJ, Alaiti RK, Vallio CS, Hespanhol L. Artificial intelligence and machine-learning approaches in sports:
Concepts, applications, challenges, and future perspectives. Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy. 2024:101083. doi:
1016/j.bjpt.2024.101083.
Puniatmaja GA, Parwati NN, Tegeh IM, Sudatha IGW. The effect of e-learning and students’ digital literacy towards
their learning outcomes. Pegem Journal of Education and Instruction. 2024;14(1):348-56.
Ghalavand H. Iranian Medical Students’ E-Learning Continuance Intention After End of COVID-19 Pandemic.
Journal of Education and Health Promotion. 2024;13(1). doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1698_22.
Abdelfattah F, Al Mashaikhya NY, Dahleez KA, El Saleh A. A systematic review of e-learning systems adoption
before and during the COVID-19. Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication. 2024;73(3):292-311. doi:
1108/GKMC-02-2022-0033.
Qazi MA, Sharif MA, Akhlaq A. Barriers and facilitators to adoption of e-learning in higher education institutions of
Pakistan during COVID-19: perspectives from an emerging economy. Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management.
;15(1):31-52. doi: 10.1108/JSTPM-01-2022-0002.
Mousavi A, Mohammadi A, Mojtahedzadeh R, Shirazi M, Rashidi H. E-learning educational atmosphere measure
(eeam): a new instrument for assessing e-students’ perception of educational environment. Research in Learning Technology.
;28(0).
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










