Identification of the Cause-and-Effect Chain (Reciprocal Relationships) of the Components Explaining the Impact of Scaffolding on Time Management, Self-Directed Learning, and Educational Quality in Lower Secondary School Students
Keywords:
Scaffolding, Time Management, Self-Directed Learning, Educational QualityAbstract
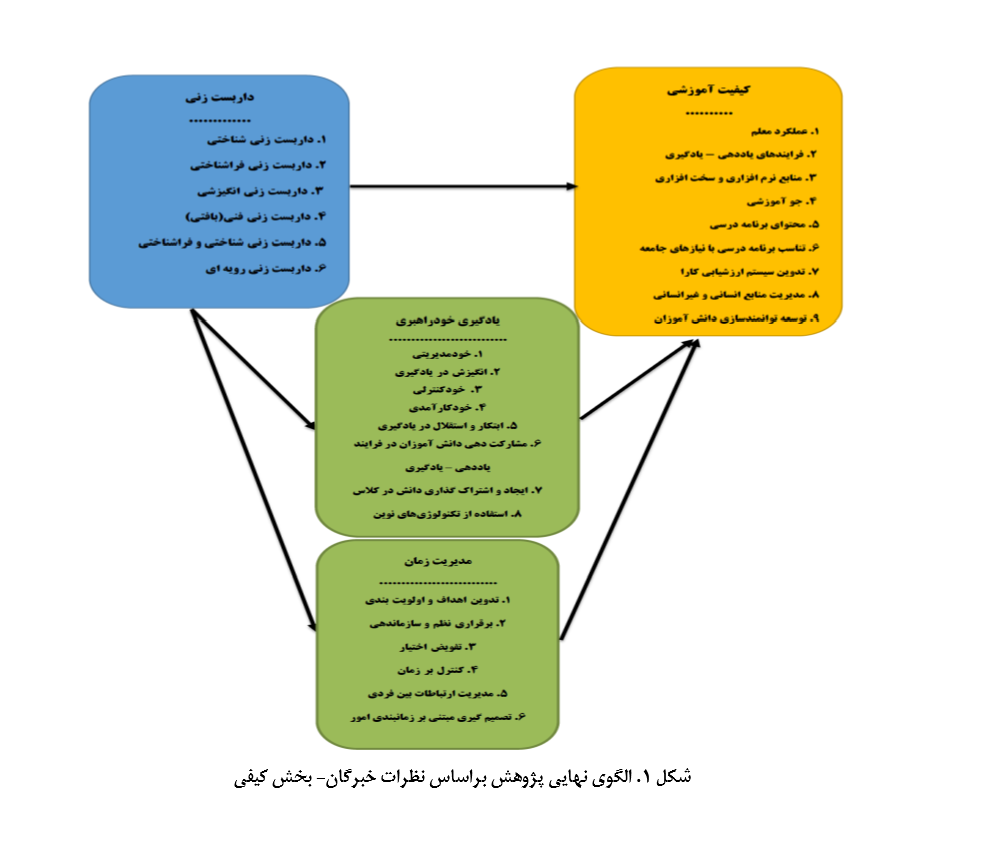
This study investigates the cause-and-effect chain of factors explaining the impact of scaffolding on time management, self-directed learning, and educational quality among lower secondary school students through an exploratory mixed-methods approach. A systematic literature review was conducted, selecting relevant studies and research models. The qualitative phase involved academic and organizational experts, while the quantitative phase included 11,836 students from urban and rural schools in Qaemshahr during the 2021-2022 academic year. In the qualitative phase, 20 participants were selected through purposive sampling, while 372 students were chosen using stratified random sampling for the quantitative phase. Additionally, 15 participants were selected for the cause-and-effect chain analysis using purposive sampling. Data collection methods included Delphi technique with structured checklists analyzed via SPSS, structural equation modeling using Smart PLS, and the DEMATEL method for cause-and-effect analysis. Findings from the qualitative phase identified six scaffolding components: cognitive, metacognitive, motivational, technical, cognitive-metacognitive, and procedural. Time management included goal setting, organization, delegation, control, interpersonal communication, and decision-making. Self-directed learning comprised self-management, motivation, self-control, self-efficacy, initiative, student participation, knowledge sharing, and technology use. Educational quality encompassed teacher performance, teaching-learning processes, resources, educational climate, curriculum content and relevance, evaluation systems, and resource management. Quantitative results demonstrated significant impacts of scaffolding on educational quality, time management, and self-directed learning. Time management and self-directed learning also significantly influenced educational quality, serving as mediators in the research model. The cause-and-effect analysis revealed that cognitive-metacognitive scaffolding, time control, student participation, and teacher performance were the most influential factors. The systematic review assessed study quality using the Glyn method, with article scores ranging from 75 to 86. Validity and reliability were confirmed using content, construct, and composite reliability methods. The findings provide valuable insights for improving educational quality through scaffolding interventions.
Downloads
References
Shafiee Roodposhti M, Ezami E, Hedayati MH, Karimi A. User-generated content effectiveness in co-creation of online higher educational services. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education. 2024. doi: 10.1080/08841241.2024.2336917.
Bazargan Harandi A. Educational Evaluation: Concepts, Models, and Operational Processes. 16th ed. Tehran: SAMT Publishing; 2018.
Okati F, Mojozi A, Pishadast A. Enhancing writing skills through scaffolding techniques: A mixed-methods study. Linguistic Research in Foreign Languages. 2022;12(3):214-37.
Hosseini Tehran AS, editor Enhancing educational quality in elementary schools in Mahshahr County2018.
Hosseini Largani SM, Mojtabizadeh M. Designing and validating a model of educational quality for universities in Iran. Management and Planning in Educational Systems. 2021;14(2):221-58. doi: 10.52547/MPES.14.2.221.
Samiei Zafarqandi M, Eyravani Manesh M. Investigating the use of scaffolding strategies in education and their impact on students' learning and retention. Journal of Education and Training. 2018;33(2):117-32.
McCloskey ML, Orr J, Stack L, Kleckova G. Scaffolding academic language for English learners: What, why, how?2010. 1-6 p.
Olson MA, Ramirez JG, Hergenhahn BR. Introduction to Theories of Learning. Tehran: Douran Publishing; 2021.
Rahimi Doost G. Effective scaffolding frameworks in problem-solving learning environments. Tehran: Doctoral dissertation, Allameh Tabataba'i University; 2013.
Rahimi Doost G, Norouzi D. Educational scaffolding strategies in problem-solving learning environments. Medical Education Strategies Bi-Monthly. 2014;7(5):345-52.
Garrison DR, Kanuka H. Blended learning: Uncovering its transformative potential in higher education. Internet and Higher Education. 2004;7(2):95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2004.02.001.
Norouzi D. Principles of Educational Design. Tehran: SAMT Publications; 2014.
Martin GL. Mathematics for Teachers. Tehran: Barhan Cultural School Publications; 2015.
Abdi A, Jahaniyan Najafabadi A. Administrative skills in school (planning, organization, time management, attention, memory, and metacognition homework). Isfahan: Publication Best Ideas; 2010.
Karimi F, Dalaver Z. The impact of time management training on self-directed learning in first-year high school female students. Curriculum Planning Research. 2015;12(47):158-67.
Naeimi E, Adelpour M. Evaluating the effectiveness of time management training on quality of life, procrastination, and decision-making among male high school students. Counseling and Psychotherapy Culture. 2020;11(43):63-88.
Zomorodian G, Ghorbani Vajargah N. The impact of time management on knowledge management processes in schools: A case study in Karaj. Business Management. 2013;5(18):85-100.
Aflaki Fard H, Akbari MR. The relationship between time management, creativity, and self-regulation among sixth-grade elementary students in Sa'dabad. Educational Research. 2019;5(18):69-90.
Naeimi L, Bigdeli S, Soltani Arabshahi K. The readiness for self-directed learning among medical students. Education Strategies in Medical Sciences. 2013;5(3):177-81.
Mathé NEH, Christensen AS. Show and tell: scaffolding practices in lower secondary social science classrooms. Journal of Curriculum Studies. 2024. doi: 10.1080/00220272.2024.2378315.
Nadi MA, Gordan Shekan M, Golparvar M. The impact of critical thinking, problem-solving, and metacognition training on self-directed learning among students. Curriculum Planning Research. 2011;8(28-29):53-61.
Afshari M, Norian M, Ahmadi A, Norouzi D. Synthesis of components and methods of self-directed learning from the perspective of the Quran. Quranic Studies Quarterly. 2019;10(39):243-70.
Laket J. Effective management. Tehran: State Management Training Center Publications; 2011.
Yukselturk E, Bulut S. Predictors for student success in an online course. Educational Technology and Society. 2007;10(2):71-83.
Hasan M. Impact of Motivational Scaffolding on the Acquisition of Writing Skills in L2 Situation. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention. 2018;7(12):39-45.
Souri M. Examining factors influencing the quality of education in Tehran's elementary schools. Educational Management Research. 2020;12(46):277-306.
Souri M, Mojtabizadeh M, Davoudi R. Designing a qualitative scaffolding model for high school students. Educational Management and Perspectives Quarterly. 2023;5(1):142-61.
Souri M, Mojtabizadeh M, Davoudi R. Identifying and validating components of scaffolding in Iran's secondary education system. Sociology of Education Quarterly. 2023;9(2):311-32.
Dominguez S, Svihla V. A review of teacher implemented scaffolding in K-12. Social Sciences & Humanities Open. 2023;8(1):100613. doi: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2023.100613.
Kim JY, Lim KY. Promoting learning in online, ill-structured problem solving: The effects of scaffolding type and metacognition level. Computers & Education. 2019;138:116-29. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.05.001.
Ghaedi Bardei M, Keyhan J. Developing a model of strategies to improve virtual education quality in primary schools using synthesis research. Innovations in Educational Management Quarterly. 2022;18(1):70-89.
Ebrahimi A, Mirshah Jafari SE, Rabani A. Identifying and explaining the essentials of self-directed teaching-learning strategies tailored to the generational characteristics of today's students. Higher Education Curriculum Studies. 2021;12(24):333-64.
Chenari ZB, Bemei L. A model for assessing educational quality in primary schools: A case study in Andimeshk County. Education and Evaluation Journal. 2020;13(52):161-85.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










