واکاوی معنای فهم در دیدگاه گادامربه منظور ارائه مدل مفهومی راهبردهای یاددهی-یادگیری
کلمات کلیدی:
فهم, هرمنوتیک, دیالوگ, گادامر, راهبردهای یاددهی-یادگیریچکیده
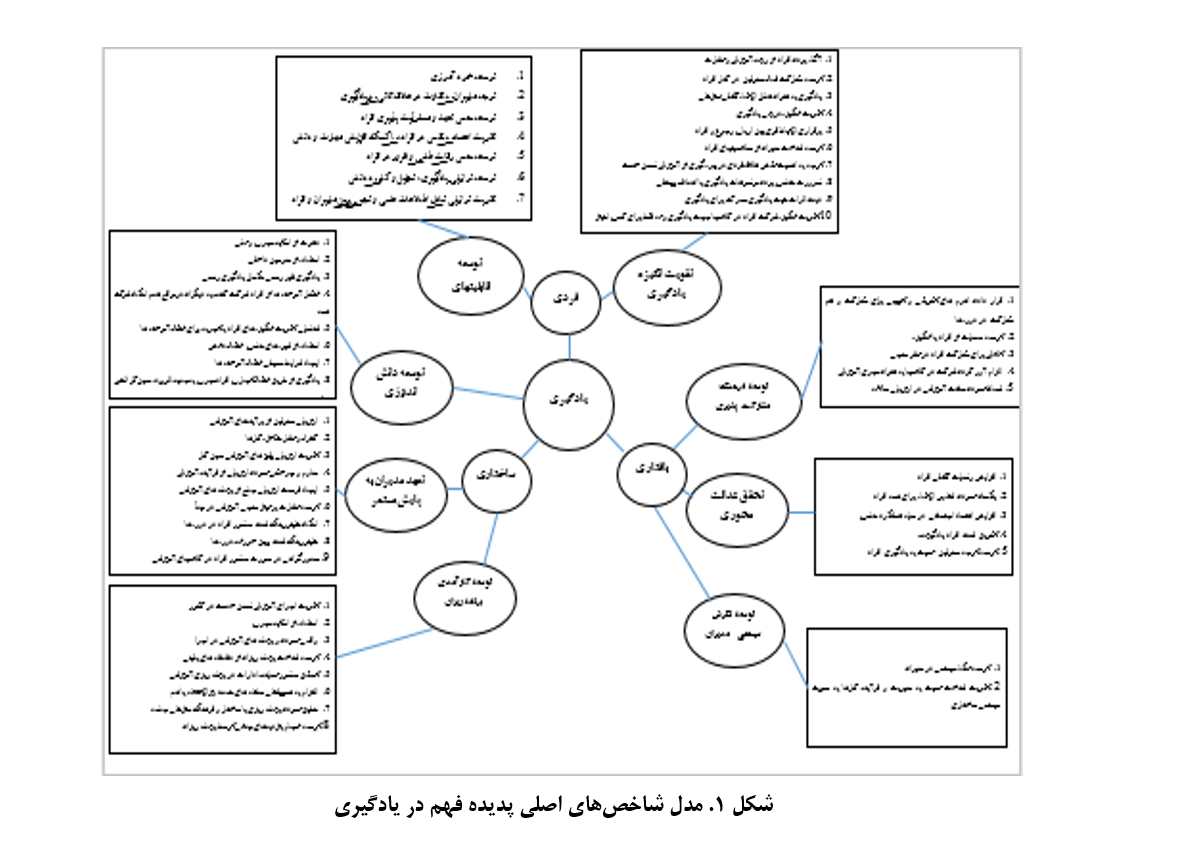
این پژوهش با هدف واکاوی معنای «فهم» در دیدگاه گادامر و کاربرد آن در ساخت مدل مفهومی یاددهی-یادگیری، به تحلیل و بررسی نظریه گادامر پرداخته است. روش پژوهش فوق مشتمل بر تحلیلی-توصیفی در ناحیه بررسی مبانی و دستاوردهای آموزشی تربیتی انتخاب شده است و در کنار تحلیل و توصیف از مصاحبه هم استفاده گردید. نتایج تحقیق نشان میدهد که نتایج واکاوی معنای فهم در دیدگاه گادامر نشان میدهد که فهم بهعنوان فرایندی پویا، تعاملی و تفسیری، میتواند چارچوبی برای طراحی راهبردهای نوین یاددهی-یادگیری فراهم کند. اصول کلیدی گادامر مانند ادغام افقها، پیشفرضها و دیالوگ نشان میدهند که یادگیری زمانی معنادار و عمیق میشود که دانشآموزان و معلمان در یک فرایند گفتوگو محور به تولید معنا بپردازند. این دیدگاه تأکید دارد که معلمان باید بهجای انتقالدهنده صرف دانش، تسهیلگر یادگیری باشند و از طریق شناخت پیشفرضهای دانشآموزان، ارتباط بین دانش پیشین و جدید را تقویت کنند. مدل مفهومی پیشنهادی این پژوهش، با تمرکز بر محیطهای تعاملی، طراحی سوالات باز و فعالیتهای مشارکتی، راهبردهایی برای تقویت تفکر انتقادی و تعامل در فرایند یادگیری ارائه میدهد. این یافتهها با نظریات دیویی و ویگوتسکی درباره یادگیری تجربی و اجتماعی همخوانی دارد اما عمق فلسفی بیشتری در تأکید بر نقش دیالوگ و تفسیر دارد و میتواند به ارتقای کیفیت آموزش در محیطهای مختلف منجر شود.
دانلودها
مراجع
Siemens G. Connectivism: A Learning Theory for the Digital Age. International Journal of Instructional Technology
and Distance Learning. 2005.
Aliakbari F, Salimzadeh M. Analysis of the concept of "dialogue" in Gadamer's hermeneutic theory and its application
in teaching-learning. Journal of Educational Studies. 2019;7(3):112-30.
Mirzaei J. Examining the impact of Gadamer's approach in curriculum design for secondary schools. Quarterly Journal
of Education. 2019;20(2):112-26.
Hosseini M, Abdollahzadeh A. Modeling teaching-learning from Gadamer's perspective in higher education. Journal
of Educational Research. 2021;15(3):45-62.
Gadamer HG. Truth and Method: Bloomsbury Academic; 2018.
Heidegger M. Being and Time: Blackwell; 1971.
Mohamadinejad M. Understanding and Hermeneutics: Gadamer's Philosophical Contribution to the Education
Theory. Journal of Educational Philosophy. 2022;30(2):99-112.
Mohammadinejad M. Educational Strategies for the Alpha Generation: Bridging Traditional and Digital Learning
Approaches. Journal of Modern Education. 2022;15(1):65-80.
Bruner J. Toward a Theory of Instruction: Harvard University Press; 1966.
Shahbazi J. Application of Gadamerian methods in teaching humanities concepts in universities. Journal of Higher
Education. 2020;14(1):88-101.
Aristotle. Nicomachean Ethics: Oxford University Press TRAN - David Ross; 2009.
Allen K, Smith J. The Dialogic Learning Environment: Applications of Gadamer's Hermeneutics in Education. Journal
of Educational Philosophy. 2020;45(2):143-57.
Ricoeur P. Hermeneutics and the Human Sciences: Cambridge University Press; 1981.
Dastneshan R, Jalali S. Investigating the impact of dialogue in teaching-learning in the digital age: A study in Iranian
schools. Journal of Educational Sciences. 2023;23(4):56-72.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 1403 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










