طراحی و اعتباریابی الگوی برنامه درسی علوم اجتماعی دوره متوسطه اول بر اساس مهارت های قرن بیست و یکم
کلمات کلیدی:
برنامه درسی, علوم اجتماعی, مهارت های قرن بیست و یکمچکیده
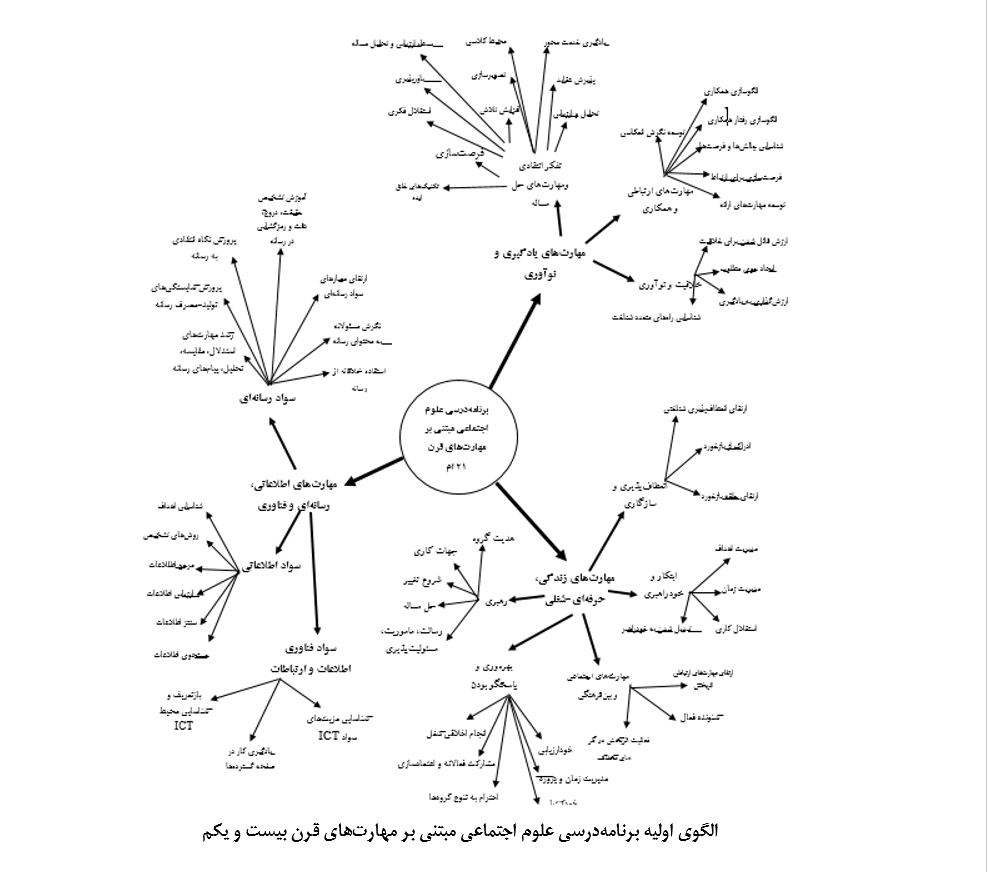
هدف پژوهش حاضر طراحی و اعتباریابی الگوی برنامهدرسی علوم اجتماعی دوره متوسطه بر اساس مهارتهای قرن بیست و یکم بود. این پژوهش از نوع توسعهای-کاربردی و بر اساس اهداف پژوهش از نوع آمیخته (کیفی و کمی) اکتشافی است. جامعه آماری مربوط به مصاحبه شامل متخصصان برنامهریزی درسی، معلمان متخصص علوم اجتماعی و سرگروههای آموزشی علوم اجتماعی بود. نمونه آماری شامل تعداد 16 نفر بود که با استفاده از روش نمونهگیری هدفمند و بر اساس معیارهای ورود و خروج به مصاحبه انتخاب شدند و تعداد نمونه آماری بر اساس اشباع دادهها تعیین شد. جامعه آماری مربوط به بخش پرسشنامه و اعتباریابی الگو نیز شامل متخصصان برنامهریزی درسی، معلمان متخصص علوم اجتماعی، سرگروههای آموزشی علوم اجتماعی و دانشجویان دکتری شهر تبریز در رشته برنامهریزی درسی بود که تعداد آنها 700 بود. نمونه آماری نیز تعداد 244 نفر بود که با استفاده از روش نمونهگیری در دسترس انتخاب شده و تعداد آنها بر اساس جدول مورگان تعیین شد. در پژوهش حاضر برای گردآوری دادههای پژوهش از سه ابزار سنتزپژوهی، مصاحبه و پرسشنامه برای گردآوری دادهها استفاده شد که روایی و پایایی آنها مورد تایید است. برای تجزیه و تحلیل دادههای پژوهش از نرمافزارهای SPSS-26 و PLS-3 استفاده شد. بر اساس یافتههای پژوهش الگوی طراحی شده برای برنامهدرسی علوم اجتماعی بر اساس مهارتهای قرن بیست ویکم دارای 3 مولفه اصلی، 11 مولفه فرعی و 58 مفهوم است که که با اطمینان میتوان گفت که هر سه مولفه و یازده زیرمولفه و 58 مفهوم کفایت لازم را برای ماندن در پژوهش دارند و بنابراین الگوی پیشنهادی پژوهش از برازش مطلوب برخوردار است. همچنین نتایج نشان داد که الگوی طراحی شده از پایایی و سازگاری درونی مطلوب برخوردار است و میتوان با اطمینان گفت که وضعیت پایایی و روایی مدل همگرایی پژوهش تایید میشود و بنابراین الگوی طراحی شده برای مولفههای برنامهدرسی علوم اجتماعی دوره متوسطه اول بر اساس مهارتهای قرن بیست و یکم از اعتبار مطلوبی برخوردار است.
دانلودها
مراجع
Stehle SM, Peters-Burton EE. Developing student 21st Century skills in selected exemplary inclusive STEM high schools. International Journal of STEM Education. 2019;6(39):1-15. doi: 10.1186/s40594-019-0192-1.
Wood L. Literacy: The role of communication skills 2017. Available from: http://www.sec-ed.co.uk/best-practice/literacy-the-role-of-communicatio n-skills/#null.
Snap P. Twenty-first century learning in the senior secondary school: a New Zealand teacher's innovation. Educational Researcher. 2021;32(1):416-24.
Hamidu HK, Péter I. The Alignment/Linkage of Students’ Academic Competence Experienced inSecondary Schools and Universities. A Case Study of Competence-BasedCurriculum Implementation in Tanzania. International Journal of Social Science and Human Research. 2025;08(02). doi: 10.47191/ijsshr/v8-i2-58.
Namubiru A, Kisembo M, Kasiita T, Kagambe E, Kasiita T. Perceptions of Teachers on the Implementation of the Competence-Based Curriculum in Secondary Schools in Bundibugyo and Ntoroko Districts, Uganda. East African Journal of Education Studies. 2024;7(3):13-27. doi: 10.37284/eajes.7.3.2013.
Štolcová K, Hanuš M, Řezníčková D. Geography Curriculum Fidelity in Map-Skills Development: Examining Teachers’ Personal Concepts, Lesson Objectives, and Observed Lessons. Geografie. 2023;128(4):397-418. doi: 10.37040/geografie.2023.016.
Knekta E, Almarlind P, Ottander C. The Purpose of Science Education. Nordic Studies in Science Education. 2022;18(1):39-62. doi: 10.5617/nordina.8224.
Mahnam Z, Mahdizadeh A, Shabani Gil Chalan H, Salimi J, Araghiyeh A. A look at critical thinking-based curriculum content in the first secondary school period. Journal of Teaching Research of Kurdistan University. 2021;9(1):255-74.
Rahimi B. A meta-analysis of challenges in the higher education environment in the 21st century as a model for curriculum orientation. Biannual Journal of Higher Education Curriculum Studies. 2018;9(17):115-66.
Mukombe C, Gaotlhobogwe M. Towards a coherent framework for infusing 21st century skills in the school curriculum. Mosenodi Journal. 2021;24(2):1-21.
Manochehri MH, Shafiei N, Mehdizadeh A, Araghieh A. Identifying the Dimensions and Components of a Systems Thinking Curriculum With a Heutagogical Approach in Lower Secondary Education. Jsied. 2025;4(5):300-14. doi: 10.61838/jsied.4.5.16.
Arabloo P, Hemmati F, Rouhi A, Khodabandeh F. The Effect of Technology-Aided Project-Based English Learning on Critical Thinking and Problem Solving as Indices of 21st Century Learning. Journal of Modern Research in English Language Studies. 2022;9(1):125-50.
Guffová D, Haviar M, Sisáková-Chovanová A. 21st Century Skills in Educational Standards for Lower Secondary Education in Slovakia. Norma. 2022;27(1):9-18. doi: 10.5937/norma27-36344.
Özen NE, Kaplan K. 21st Century Skills in Curriculums of Turkey, Alberta, Korea and Singapore. Pamukkale University Journal of Education. 2023. doi: 10.9779/pauefd.1182195.
Bhowa M, Aribino N. Education With Production or Education Pragmatism as Solution to the Skills Shortage in Zimbabwe: Policy With Continuity? Lh. 2024:136-60. doi: 10.71458/pwt67g20.
Louis AT, Thompson P, Sulak TN, Harvill ML, Moore ME. Infusing 21st Century Skill Development into the Undergraduate Curriculum: The Formation of the iBEARS Network. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education. 2021;22(2):1-8. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.00180-21.
Rebecca J. Effective Assessment of Generic Skills in Uganda's Secondary Schools. East African Journal of Arts and Social Sciences. 2025;8(1):221-3. doi: 10.37284/eajass.8.1.2711.
Hörmann C, Schmidthaler E, Sabitzer B. Navigating The Implementation Of the Curriculum Digital Education In Austrian Secondary Schools: Challenges And Teacher Perspectives. 2023:167-79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44900-0_13.
Mpisili M. Innovation and Strategic Management Practices in the Implementation of Competency-Based Curriculum in Kenya. International Journal of Current Aspects. 2022;6(1):62-72. doi: 10.35942/ijcab.v6i1.241.
Putra M, Kampai A, Ngardi V. Revolusi Pendidikan Menengah Di Amerika: Peran Hidden Curriculum Dalam Menghadapi Tantangan Era Industri 5.0. Jemast. 2024;3(02):125-35. doi: 10.57255/jemast.v3i02.852.
Schoots-Snijder AJM, Tigelaar DE, Admiraal W. Curriculum Guidelines for the Development of Student Agency in Secondary Education: A Systematic Review. The Curriculum Journal. 2025. doi: 10.1002/curj.318.
Sapkota A. Relevancy of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy in School-Level English Language Curriculum. NELTA Bagmati J. 2022;3(1):19-40. doi: 10.3126/nbj.v3i1.53413.
SarigÖZ O. Examination of Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum in Terms of 21st Century Skills. E-International Journal of Educational Research. 2023. doi: 10.19160/e-ijer.1200499.
Athanasiadis A. The Importance of Artificial Intelligence in the High School Computer Science Curriculum as Evaluated by Computer Science Teachers in the Region of Western Macedonia. Ijei. 2024;6(4):93-102. doi: 10.69685/nrjm3891.
Sumen OO, Calishici H. Examining the 21st Century Skills of Secondary School Students: A Mixed Method Study. Journal of Education & Social Policy. 2017;4(4):92-100.
Baratali M, Karimian Khuzani S. Content analysis of the work and technology curriculum for the first secondary school period, from the perspective of information and communication technology literacy, based on 21st-century digital skill and proficiency indicators. Tehran2018.
Kabir SMA. Policy and Practice of Listening in Secondary English Education: A Critical Reflection From Bangladesh. Mj. 2024;48(3):1-11. doi: 10.61871/mj.v48n3-13.
Ruzeika FF, Mohammed LA, George P. Challenges Faced by Students in the Application of CBE in Senior Secondary Mathematics Education in Sri Lanka. JLSDGR. 2024;5(2):e03021. doi: 10.47172/2965-730x.sdgsreview.v5.n02.pe03021.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Farahnaz Kohi Somee (Author); Hosein Baghaee (Corresponding author); Zarrin Daneshvar Heris (Author)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










