اثربخشی بازآموزی اسنادی بر تعلل ورزی تحصیلی دانش آموزان دختر کلاس ششم ابتدایی
کلمات کلیدی:
بازآموزی اسنادی, تعلل ورزی تحصیلی, دانش آموزان کلاس ششم ابتداییچکیده
مقدمه: هدف اصلی این پژوهش بررسی اثربخشی بازآموزی اسنادی بر تعلل ورزی تحصیلی دانشآموزان دختر پایه ششم دورهي ابتدایی بود.
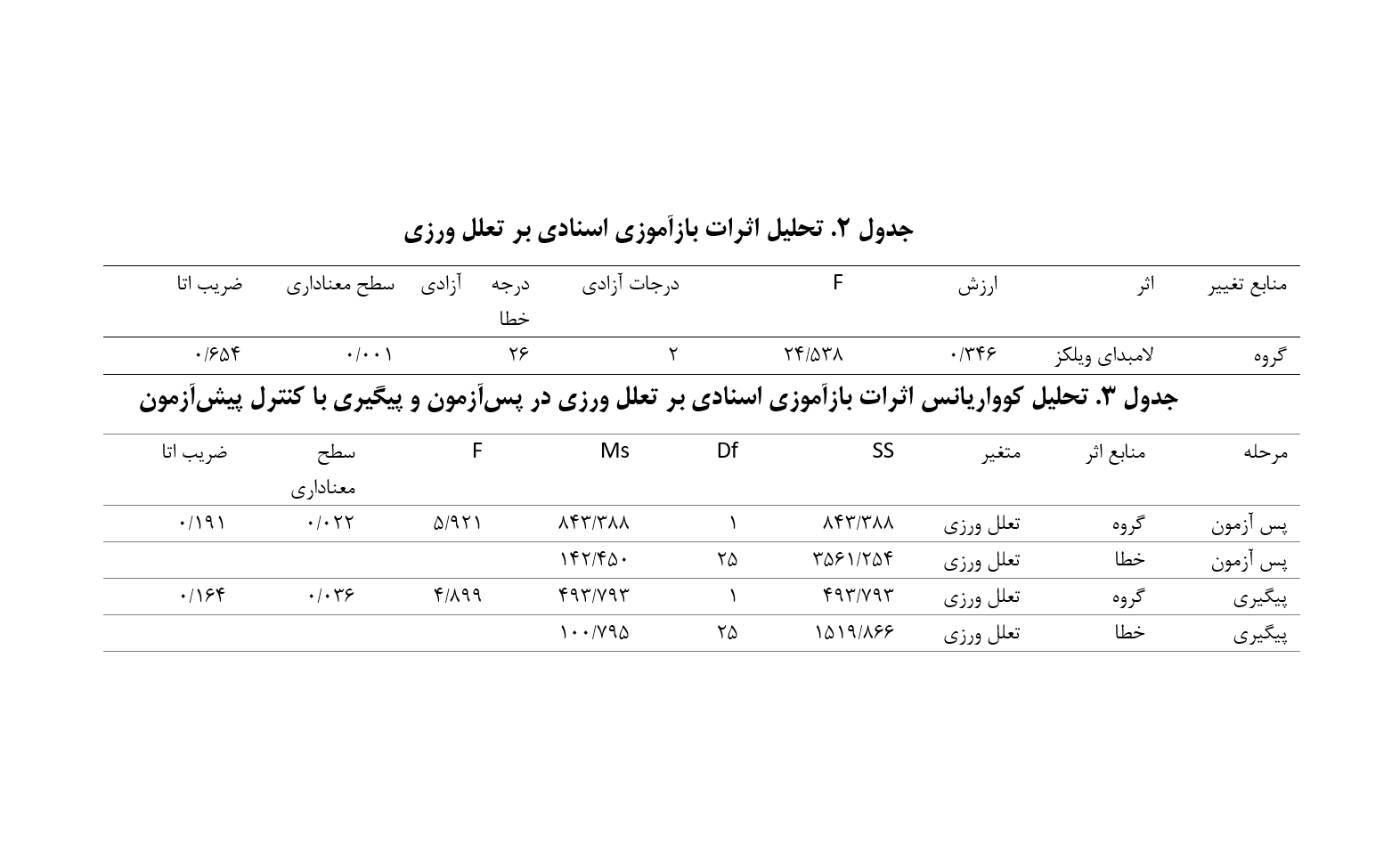
روش کار: طرح پژوهش از نوع مطالعهی نیمه آزمایشی با طرح پیشآزمون–پسآزمون با گروه گواه و مرحله پیگیری بود. جامعه آماري شامل تمام دانشآموزان دختر پایه ششم ابتدایی شهر همدان بود که در سال تحصیلی 99-98 مشغول به تحصیل بودند. از این میان براي انجام آموزش بازآموزي اسنادي، 30 دانش آموز دختر پایه ششم ابتدایی که در سال تحصیلی 99-98 مشغول به تحصیل بودند به صورت در دسترس انتخاب شدند و در دو گروه آزمایشی 15 نفر و گروه گواه 15 نفر گمارده شدند. آزمودنیها به مقیاس اندازه گیری تعلل ورزی تحصیلی نسخه دانش آموز (PASS (1984) برای اندازه گیری تعلل ورزی به عنوان پیشآزمون و سپس پسآزمون و مرحله پیگیری پاسخ دادند. سپس، گروه آزمایش 11 جلسهی 45 دقیقهای آموزش باز آموزی اسنادی که توسط سلیگمن و همکاران (1996) طراحی شده را دریافت کردند؛ در حالی که گروه کنترل هیچ آموزشی را دریافت نکرد. دادهها با استفاده از تحلیل کوواریانس تجزیه و تحلیل شدند.
نتایج: نتایج بیانگر این بود که بازآموزی اسنادی بر کاهش تعلل ورزی تحصیلی به طور معناداری موثر بوده است (01/0>p).
نتیجه گیری: بر اساس نتایج پژوهش حاضر، میتوان گفت که، بازآموزی اسنادی میتواند بهعنوان یک گزینه آموزشی موثر برای کمک به دانشآموزان جهت کاهش تعلل ورزی آنان مورد استفاده قرار گیرد.
دانلودها
مراجع
Matteucci MC. Attributional retraining and achievement goals: An exploratory study on theoretical and empirical
relationship. European Review of Applied Psychology. 2017;67(5):279-89. doi: 10.1016/j.erap.2017.08.004.
Munda X, Tiwari VK. The Impact of Academic Procrastination on Students' Performance in Indian School Education
Systems: A Special Research Analysis-Vision 2045. 2024.
Sparfeldt JR, Schwabe S. Academic procrastination mediates the relation between conscientiousness and academic
achievement. Personality and Individual Differences. 2024;218:112466.
Steel P, Klingsieck KB. Academic procrastination: Psychological antecedents revisited. Australian Psychologist.
;51(1):36-46. doi: 10.1111/ap.12173.
Owens SG, Bowman CG, Dill CA. Overcoming Procrastination: The Effect of Implementation Intentions. Journal of
Applied Social Psychology. 2018;38(2):366-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2007.00309.x.
Rozental A, Forsstrom D, Lindner P, Nilsson S, Mårtensson L, Rizzo A. Treating procrastination using cognitive
behavior therapy: A pragmatic randomized controlled trial comparing treatment delivered via the internet or in groups. Behavior
Therapy. 2018;49(2):180-97. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2017.08.002.
Rosa M, Pazos S, de-Cozar RS. Interventions to reduce academic procrastination: A systematic review. International
Journal of Educational Research. 2023;121:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ijer.2023.102228.
Grund A, Fries S. Understanding procrastination: A motivational approach. Journal of Personality and Individual
Differences. 2018;121:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.09.035.
Pasalari M. Effect of attributional retraining on optimism, academic procrastination Ahwaz elementary students:
Persian Gulf University; 2020.
Parker PC, Perry RP, Chipperfield JG, Hamm JM, Pekrun R. An attribution-based motivation treatment for low control
students who are bored in online learning environments. Motivation Science. 2018;4(2):177-90. doi: 10.1037/mot0000081.
Morris M, Tiggemann M. The impact of attributions on academic performance: A test of the reformulated learned
helplessness model. Social Sciences Directory. 2013;2(2):3-15. doi: 10.7563/SSD_02_02_01.
Weiner B. The development of an attribution-based theory of motivation: A history of ideas. Educational Psychologist.
;45(1):28-36. doi: 10.1080/00461520903433596.
Li Y, Lan J, Ju C. Achievement motivation and attributional style as mediators between perfectionism and subjective
well-being in Chinese university students. Personality and Individual Differences. 2015;79:146-51. doi:
1016/j.paid.2015.01.050.
Sukariyah MB, Assaad G. The effect of attribution retraining on the academic achievement of high school students in
mathematics. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015;177:345-51. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.02.356.
Scheier MF, Carver CS. Optimism, coping, and health: assessment and implications of generalized outcome
expectancies. Health Psychology. 1985;4(3):219. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.4.3.219.
Parsafar A. Investigating the Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing on Social Anxiety and Academic
Procrastination Among Students. Jayps. 2024;5(3):55-64. doi: 10.61838/kman.jayps.5.3.6.
Alipour F, Farid A, Mosleh SQ. The model of academic procrastination based on academic self-handicapping and
perfectionism with the mediating role of students' sense of competence. Research in Cognitive and Behavioral Sciences.
;13(2):1-20.
Emami Khotbesara Z, Mahdian H, Bakhshipour A. Comparing the Effectiveness of Academic Buoyancy and
Psychological Capital Training on Academic Procrastination in Female High School Students. Iranian Journal of Educational
Sociology. 2024;7(3):149-60. doi: 10.61838/kman.ijes.7.3.18.
Joojam P, Safarpour-Dehkordi S. The Effect of Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies on Self-Concept and
Academic Procrastination in Middle School Students. Excellence in Education Quarterly. 2024;3(2):6-10.
Liu Y, Zhou F, Zhang R, Feng T. The para-hippocampal-medial frontal gyrus functional connectivity mediates the
relationship and influence of optimism and procrastination by cognitive-behavioural attribution oriented training. Behavioural
Brain Research. 2023;48:44-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114463.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 نشریه پژوهش و نوآوری در تربیت و توسعه

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










