شناسایی عوامل کاهش ترک خدمت معلمان دوره ابتدایی با رویکرد تحلیل مضمون
کلمات کلیدی:
ترک خدمت, ماندگاری معلمان, تحلیل مضمون, عوامل سازمانی, معلمان دوره ابتداییچکیده
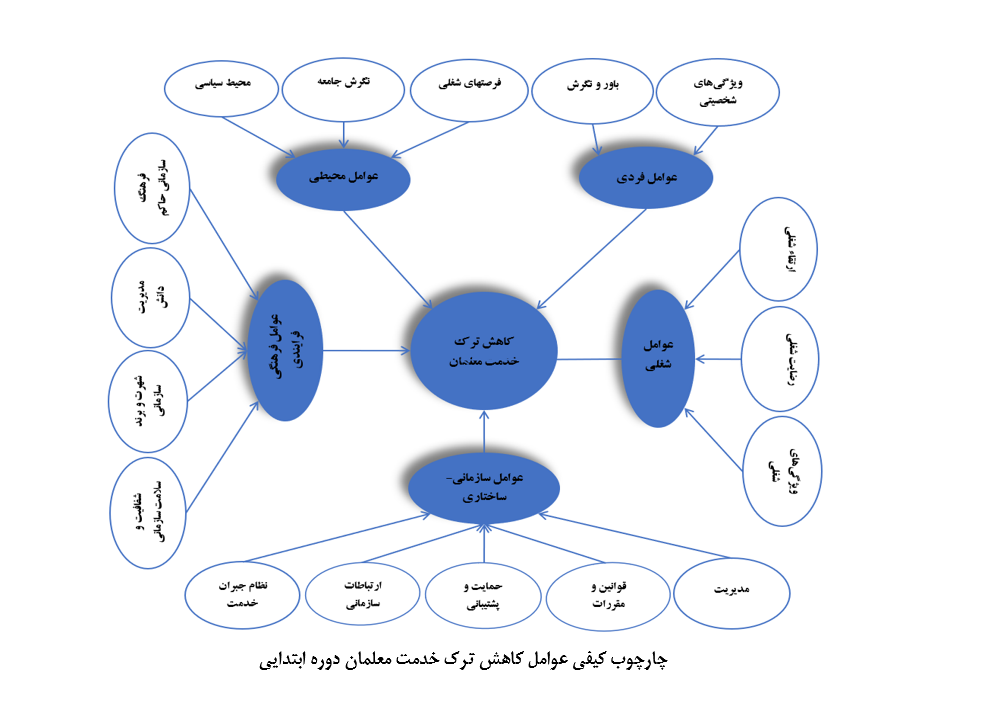
هدف این پژوهش شناسایی عوامل کاهشدهنده ترک خدمت معلمان دوره ابتدایی و ارائه یک چارچوب کیفی جامع مبتنی بر تحلیل مضمون است. پژوهش از نظر هدف کاربردی و از نظر روش کیفی–اکتشافی با رویکرد استقرایی انجام شد. دادهها از طریق مطالعات اسنادی و مصاحبههای نیمهساختاریافته با ۳۲ نفر از خبرگان دانشگاهی و متخصصان آموزشوپرورش گردآوری شد و تا رسیدن به اشباع نظری ادامه یافت. تحلیل دادهها با استفاده از تحلیل مضمون و کدگذاری در سطوح مضامین پایه، سازماندهنده و فراگیر و با بهرهگیری از نرمافزار MAXQDA انجام گرفت. اعتبار یافتهها با معیارهای اعتمادپذیری، باورپذیری، تأییدپذیری و انتقالپذیری بررسی شد. نتایج نشان داد عوامل کاهش ترک خدمت معلمان در قالب ۵ مضمون فراگیر، ۱۸ مضمون سازماندهنده و ۹۲ مضمون پایه قابل تبیین است. این مضامین فراگیر شامل عوامل فردی، شغلی، سازمانی–ساختاری، فرهنگی–فرایندی و محیطی هستند که بهصورت تعاملی بر ماندگاری معلمان اثر میگذارند. نتایج بر ضرورت رویکردی چندبعدی و نظاممند در سیاستگذاری منابع انسانی آموزشوپرورش تأکید دارد و نشان میدهد مداخلات یکبعدی قادر به کاهش پایدار ترک خدمت معلمان نیستند.
دانلودها
مراجع
Shafique M, Fatima M, Shafique A. Employee Turnover Models: A Review of Conventional and Contemporary Approaches and Future Research Direction. Leadership and Organizational Behavior Journal. 2025;4(1):42-60.
Wijayanthi IAT, Subagio M, Suhendra A, Hartini, Darmawan AA. Employee Retention Implementation Prevents Employee Turnover. SJAM. 2024;2(2):288-301. doi: 10.38035/sjam.v2i2.
Domurath A, Taggar S, Patzelt H. A contingency model of employees' turnover intent in young ventures. Small Bus Econ. 2023;60:901-27. doi: 10.1007/s11187-022-00629-2.
Arnold B, Rahimi M. Teachers' working conditions, wellbeing and retention: an exploratory analysis to identify the key factors associated with teachers' intention to leave. The Australian Educational Researcher. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s13384-024-00794-1.
Moran A, Orly L, Miriam S. Professional Commitment and Turnover Intentions of Elementary School Teachers During Educational Crisis. Front Educ. 2025;10. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1548359.
Wang G. Teaching autonomy and teachers' turnover intentions under the labor process theory perspective: A moderated mediation model of work alienation and professional identity. Teaching and Teacher Education. 2025;159:104981. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2025.104981.
Farahmandpour Z, Voelkel R. Teacher Turnover Factors and School-Level Influences: A Meta-Analysis of the Literature. Education Sciences. 2025;15(2):219. doi: 10.3390/educsci15020219.
Bustillo JCM. Optimization-based Techniques Prediction Model in Determining Employee Turnover. Procedia Computer Science. 2025;252:440-9. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2025.01.003.
Park J, Yituo Feng Y, Jeong SP. Developing an advanced prediction model for new employee turnover intention utilizing machine learning techniques. Scientific Reports. 2024;14:1221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50593-4.
Kanuto AE. Identifying Patterns and Predicting Employee Turnover Using Machine Learning Approaches. International Journal of Science and Business. 2024;36(1):20-35. doi: 10.58970/IJSB.2373.
Ebrahimi K. Investigation of the tendency and causes of employee turnover in organizations of Tehran province's counties. 2023.
Kavoosi SE, Fani AA, Danaeifard H, Nayeri S. Explaining the causes of employee turnover in Iranian knowledge-based companies and providing solutions: Investigating the role of compensation. Public Management Research. 2021;14(53):89-114.
Hashem Zehi R, Najaf Beygi R, Zabihi MR. Designing a knowledge employee turnover model in Khorasan Razavi Oil Products Distribution Company. Human Resource Management in the Oil Industry. 2021;12(47):23-39.
Miri B, Ghorbanizadeh V, Seyyed Naghavi M. Phenomenological analysis of employee turnover experience in a government organization. Management and Development Process. 2021;34(3):113-42. doi: 10.52547/jmdp.34.3.113.
Nikkhah Farkhani Z, Nemati Daghiyan S, Molamohammad Zamani M, Sheikhzadeh M. Explaining the work experience of teachers in deprived areas with the mediating role of job characteristics. Educational and School Studies. 2022;11(2):299-324.
Khanifar H, Naderi Beni N, Ebrahimi S, Fayazi M, Rahmati M. Identify the competency of schoolmasters for use in the assessment center. Journal of School Administration. 2019;7(1):105-25.
Aulia N, Haerani I. Teacher Retention and Turnover: Exploring the Factors that Influence Teacher Decision-Making. Journal of Education Review Provision. 2022;2(2):36-42. doi: 10.55885/jerp.v2i2.155.
Sudrajat J, Loke SH, Syafwandi, Bahri ES, Permana IA. A Proposed Conceptual Model of Teacher Turnover Intention in the Vocational High Schools in Indonesia. BRILLIANT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MANAGEMENT AND TOURISM(BIJMT). 2022;2(3):239-50. doi: 10.55606/bijmt.v2i3.817.
Bussin M, Brigman N. Evaluation of remuneration preferences of knowledge workers. SA Journal of Human Resource Management. 2019;17(1):1-10. doi: 10.4102/sajhrm.v17i0.1075.
Shareef RA, Atan T. The influence of ethical leadership on academic employees' organizational citizenship behavior and turnover intention: Mediating role of intrinsic motivation. Journal of Management Decision. 2019;57(3):583-605. doi: 10.1108/MD-08-2017-0721.
Aburumman O, Salleh A, Omar K, Abadi M. The impact of human resource management practices and career satisfaction on employee's turnover intention. Management Science Letters. 2020;10:641-52. doi: 10.5267/j.msl.2019.9.015.
Ready DA, Conger JA. Make your company a talent factory. Harvard Business Review. 2017:69-77.
Pirayesh R, Khan Mohammadi M, Badfar O. Factors affecting employees' intention to leave and its impact on the efficiency of Zarrin Roy Zanjan Company employees. Bimonthly Scientific-Specialized Journal of Applied Studies in Management and Development Sciences. 2020;5(1):7-18.
Basti S, Delkhah J, Danaeifard H, Fani AA. Designing a model of voluntary employee turnover. Executive Management Research Journal. 2022;14(27):375-410.
Sha'af A'mal M, Vedadi A, Tavakoli M, Gholamzadeh D. Presenting a model of elite turnover factors in the Iranian Offshore Oil Company. Quarterly Journal of Management and Education Outlook. 2024;6(1):189-210.
Oh J. Employee perceptions of HRM practices and their turnover intentions: evidence from South Korea. Journal of Evidence-based HRM. 2020;3:145-60. doi: 10.1108/EBHRM-04-2019-0037.
Lin W, Deng M. Turnover intention predictors among social workers in China. Asian Social Work and Policy Review. 2019;13(1):117-23. doi: 10.1111/aswp.12161.
Johannes Masenya JM, Ngoepe M, Jiyane V. Determinants of Turnover Intentions of Librarians at the City of Johannesburg Libraries in Gauteng Province, South Africa. South African Journal of Libraries and Information Science. 2020;86(1):73-83. doi: 10.7553/86-1-1890.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Hassan Dadashi (Author); Fakhreddin Ahmadi (Corresponding author); Hamid Shafizadeh (Author)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










