Designing a Model for Creativity Development for Primary School Students (Case Study: Tehran’s Education System)
Keywords:
creativity, causal factors, interventionist , contextual conditions , strategies, consequences , external dataAbstract
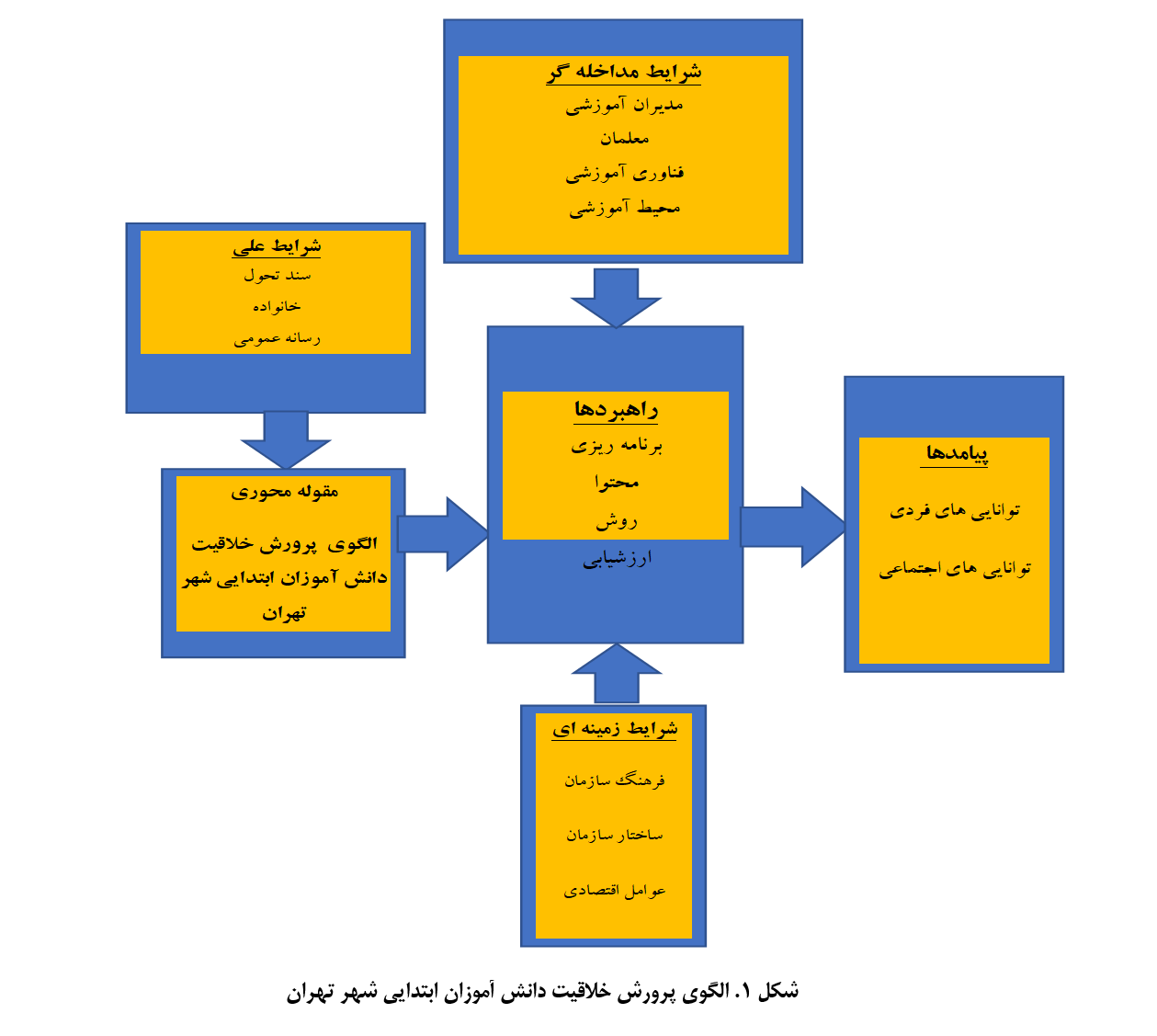
The aim of the study is to design a model for the development of creativity in primary school students in Tehran. The research method is applied in terms of its objective, qualitative in terms of data type, and a systematic grounded theory (paradigmatic) approach in nature. The target population of the study includes experts in the fields of educational sciences and psychology. Using a purposive sampling method of the theoretical type and based on theoretical saturation, 15 experts were selected for interviews. The research instrument was a semi-structured interview, during which the dimensions, components, and indicators of the model for developing creativity in Tehran’s primary school students were outlined. Initially, in-depth interviews with the experts were conducted to develop the interview form. Subsequently, open coding was used to extract the indicators, which were categorized into components and indicators using axial coding. The identified components and indicators were then sent to 15 experts for further analysis through selective coding, interviews, and brainstorming sessions. Consequently, the model was finalized with 5 dimensions, 16 components, and 102 indicators for fostering creativity in primary school students. After final validation and prioritization by the experts, the dimensions, components, and structural indicators of the model were drawn and revalidated by the experts.
Downloads
References
Robinson K, Aronica L. Creative Schools. Tehran: Tik and Avaye Noor Publishing; 2020.
Mohammadi L, editor The role of teaching methods in fostering creativity among elementary students. First
International Conference on Psychology, Educational Sciences, and Social Studies; 2018; Hamadan.
Soudagar E, editor Examining the impact of teachers' information literacy on fostering creativity among elementary
students in Hamoun. Fifth National Conference on New Approaches in Education and Research; 2020; Mahmoudabad.
Safaee N, Zarei E, Samavi A. Designing and modeling a curriculum based on creative thinking skills for elementary
school students. Educational Technologies. 2021;15(3):579-90.
Ranjbar M, editor The impact of art on teaching, learning, and fostering creativity in students. Third International
Conference on Psychology, Educational Sciences, and Social Studies; 2020; Hamadan.
Bereczki EO, Kárpáti A. Teachers' beliefs about creativity and its nurture: A systematic review of the recent research
literature. Educational Research Review. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2017.10.003.
Avila HA. Creativity in the English class: Activities to promote EFL learning. How. 2019;22(2):91-103. doi:
19183/how.22.2.141.
Białkiewicz A. Architectural competitions support student creativity. World Transactions on Engineering and
Technology Education. 2020;18(2):157-62.
Cenberci S. The Investigation of the Creative Thinking Tendency of Prospective Mathematics Teachers in Terms of
Different Variables. Journal of Education and Training Studies. 2018;6. doi: 10.11114/jets.v6i9.3434.
Baqaei H, Akbari S, Toloui L, editors. Creativity and innovations in schools. The First International Conference on
Sociology, Social Sciences, and Education with a Future Perspective; 2023; Bushehr.
Salehi Nia M, Bashghareh V, Karimi E, Ahmadi M. Investigating the role of leadership and educational management
in creativity and innovation. New Research Approaches in Management Sciences. 2023(39):45-68.
Fakhari Mobarakeh F, Etemadi Ahari A, Saber Gorgani A. A creative teaching model for elementary students
(emphasizing sixth-grade students). Leadership and Educational Management Quarterly. 2022;12(1):197-228.
Jae Hwa L, Soyeon L. Relationships between physical environments and creativity: A scoping review. Thinking Skills
and Creativity. 2023;48. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2023.101276.
Sonja V. Development of creativity in elementary school. Journal of Creativity. 2023;33(2):33-48. doi:
1016/j.yjoc.2023.100055.
Sari FW. Inquiry Based Teaching in Writing Classroom: the Effectiveness to the Students' Creativity. Journal of
English Language Teaching and Islamic Integration (JELTII). 2020;3(01):244-64.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










