Investigating the Relationship Between Contextual Factors and Academic Achievement of Fourth Grade Students: A Mixed Methods Study Using Iranian TIMSS 2019 Data
Keywords:
Contextual factors, Academic achievement, Fourth-grade students, TIMSS 2019Abstract
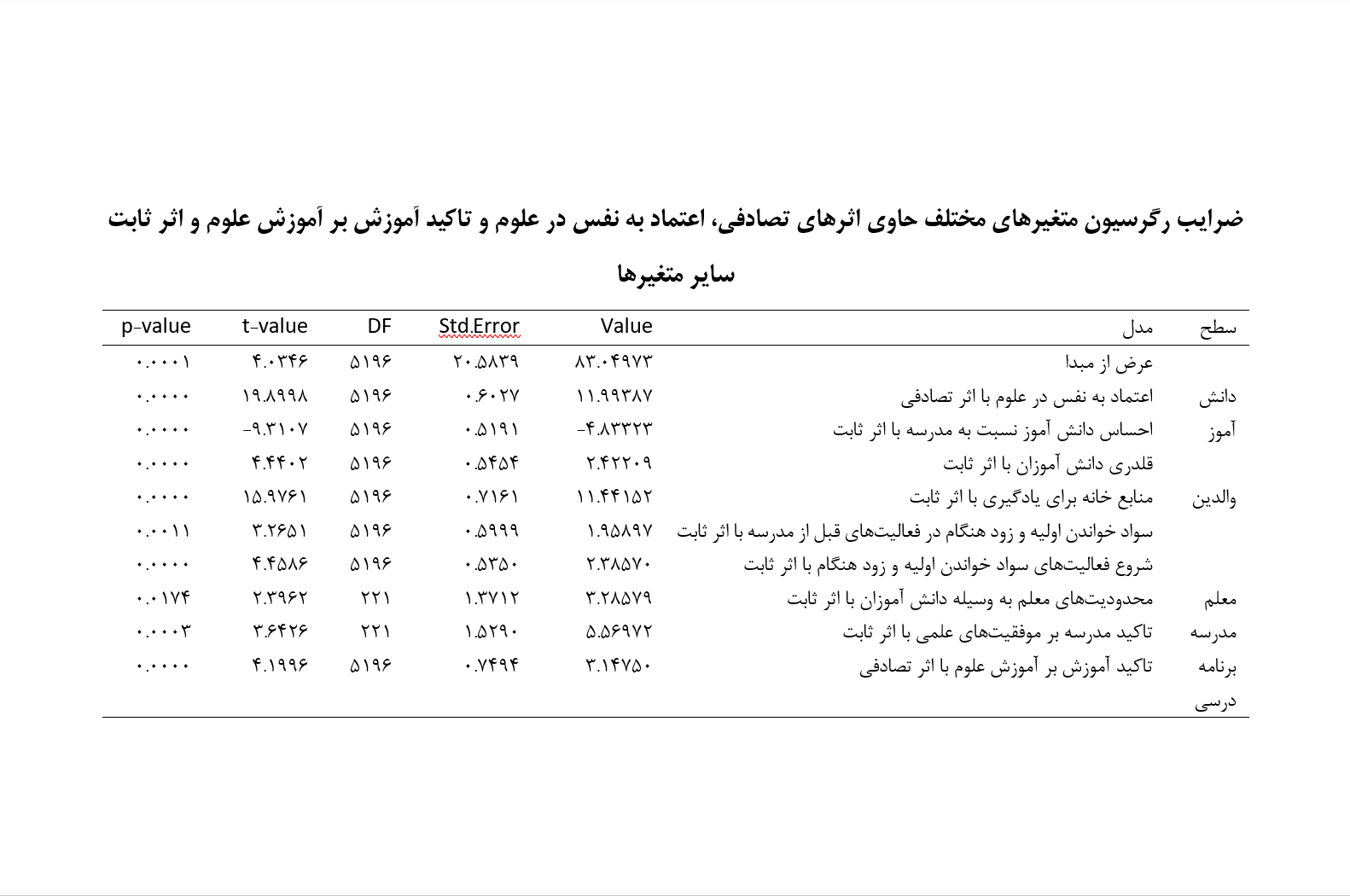
The aim of this research was to examine the relationship between contextual factors and the academic achievement of fourth-grade students, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with Iranian TIMSS 2019 data. The research was applied in nature, and methodologically, it followed a descriptive survey design. The statistical population included all Iranian fourth-grade students, both boys and girls, who participated in the TIMSS 2019 assessment. The sample consisted of 224 schools and a total of 6,010 fourth-grade students (boys and girls), with an average age of 10.2 years, who took part in the TIMSS 2019 study. To collect the necessary data regarding students' academic achievement in mathematics and science, TIMSS 2019 employed the student achievement test booklets and associated questionnaires related to five domains: curriculum, school, teacher, student, and parents. This included five test booklets for mathematics and science and five background questionnaires. The data analysis was conducted using correlation methods and multilevel regression, utilizing R software and the lmeR package. Reliability was assessed through Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. The results showed that the student-level, parent-level, teacher-level, school-level, and curriculum-level variables had a significant relationship with mathematics achievement, and these relationships varied at the school (class) level (P ≤ 0.01). Similarly, the student-level, parent-level, teacher-level, school-level, and curriculum-level variables had a significant relationship with science achievement, and these relationships also varied at the school (class) level (P ≤ 0.01).
Downloads
References
Zia Nejad Shirazi A, Goltash A. Examining the Role of Content Changes in the Curriculum on the Performance of
Fourth-Grade Students in International TIMSS Tests. Quarterly Journal of New Approaches in Educational Management.
;9(4):Winter-2018.
Mullis IVS, Martin MO, Loveless T. 20 Years of TIMSS International Trends in Mathematics and Science
Achievement Curriculum, And Instruction. 2016.
Norouzi S. Examining Factors Affecting the Progress of Iranian Students in TIMSS 2011 Science Test for Eighth
Grade (Third Year of Guidance). 2016.
Ahmadi G, Kabiri M, Naghband M. Identifying Some Misunderstandings of Fourth-Grade Elementary Students in the
Subject of Experimental Sciences Based on TIMSS 2015 Study. Quarterly Journal of Research in Educational Systems.
;14(48):127-43.
Soodkhah Mohammadi R, Shafiei B. A Look at TIMSS and Changes in the Seventh-Grade Mathematics Textbook to
Improve Results in TIMSS 2015. 2018.
Tarbiatnejad H, Salehi A, editors. Content Analysis of the Fourth-Grade Elementary Science Textbook: William Rumi
and Bloom's Method2018.
TIMSS T. A Brief Report on Preliminary Results of TIMSS 2019. 2019.
Dalia MA, Alotaibi. Computational Thinking Skills and its Impact on TIMSS Achievement: An Instruction Design
Approach. TIMSS. 2019. doi: https://doi.org/10.2458/azu_itet_v7i1_alyahya.
Danai Zarchi R, Zendavalian Naeini A, Kian M. Comparative Analysis of the Fourth-Grade Mathematics Curriculum
in Iran with Leading Countries in the TIMSS International Test. Quarterly Journal of Iranian Comparative Education.
;2(2):207-29.
Martins L, Veiga P. Do inequalities in parents education play an important role in PISA students mathematic
achievement test score disparities? Economics of Education Review. 2010;29(6):1016-33.
Mullis IVS, Martin MO. TIMSS 2015 Assessment Frameworks. 2013.
Pinheiro J, Bates D, Team RC. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R package version 3.1-163.
CRAN.R-project; 2023.
Santrock JW. Educational Psychology: McGraw Hill Higher Education; 2009.
Seventika SY, Sukestiyarno YL, Scolastica M, editors. Critical Thinking analysis based On Facione (2015)- Angelo
(1995) Logical Mathematics material of vocational high school2018.
Steinberg BFL, Dornbusch S. Negative Impact of Part-Time Work on Adolescent Adjustment: Evidence from a
Longitudinal Study. Developmental Psychology. 1993;29(2):171-80. doi: https://doi.org/10.1037//0012-1649.29.2.171.
Weissbourd R, Bouffard SM, Jones SM. School Climate: Practices for Implementation and Sustainability. New York,
NY: National School Climate Center; 2013.
Wu M. A Comparison of PISA and TIMSS 2003 Achievement Result in Mathematics. Prospect. 2009;39(1):33-46.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-009-9109-y.
Yoshino A. The Relationship Between Self-Concept and Achievement in TIMSS 2007: A Comparison Between
American and Japanese Students. International Review of Education. 2012;58(2):199-219. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11159-
-9283-7.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Study and Innovation in Education and Development

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










